# Chainlink VRF in a Smart Contract In this lesson, we will write a Chainlink VRF consumer smart contract. This contract is a fun little demo that shows you how to "roll a dice" in a smart contract. This is useful in many gaming applications, but the purpose is to show you how to implement VRF in a smart contract. Note: as always, if you want to skip the code explanation, it is optional, so please do so and go straight to deploying the contract. If you are a developer (or an aspiring one), I recommend you read through the explanation. ## Writing a VRF consumer smart contract Let's write a smart contract that gets a random number, uses that to mimic rolling a 4 sided die, and then assigns the roll to a Hogwarts House for the roller. Open [Remix](remix.ethereum.org) and create a new workspace called "VRF", create a folder called `contracts` and a file called `HousePicker.sol` inside this folder. In this file, paste the code from the `HousePicker.sol` file in the [course code repo](https://github.com/ciaranightingale/chainlink-fundamentals-code/blob/main/vrf/HousePicker.sol). ### Code Walkthrough #### Imports ```solidity import {VRFConsumerBaseV2Plus} from "@chainlink/contracts@1.3.0/src/v0.8/vrf/dev/VRFConsumerBaseV2Plus.sol"; import {VRFV2PlusClient} from "@chainlink/contracts@1.3.0/src/v0.8/vrf/dev/libraries/VRFV2PlusClient.sol"; ``` - `VRFConsumerBaseV2Plus`: Abstract contract that VRF consumer contracts need to inherit. - `VRFV2PlusClient`: Library with structs and helpers for VRF requests. #### Contract declaration ```solidity contract HousePicker is VRFConsumerBaseV2Plus {} ``` Inherits from `VRFConsumerBaseV2Plus` to be VRF compatible. #### Constant and state variables ```solidity uint256 private constant ROLL_IN_PROGRESS = 4; // value out of range of houses uint256 public s_subscriptionId; address public constant VRF_COORDINATOR = 0x9DdfaCa8183c41ad55329BdeeD9F6A8d53168B1B; bytes32 public constant KEY_HASH = 0x787d74caea10b2b357790d5b5247c2f63d1d91572a9846f780606e4d953677ae; uint32 public callbackGasLimit = 40000; uint16 public requestConfirmations = 3; uint32 public numWords = 1; mapping(uint256 => address) private s_rollers; mapping(address => uint256) private s_results; ``` - `ROLL_IN_PROGRESS`: Constant used to track when a roll is being processed. It is a `uint256` that is larger than the highest possible index. - `s_subscriptionId`: The Chainlink VRF subscription ID. - `VRF_COORDINATOR`: Address of the VRF coordinator contract on Sepolia. - `KEY_HASH`: Identifies the VRF gas lane to use. Picking a specific gas lane means picking the maximum gas price you are willing to pay for a request in gwei. Visit the [supported networks page](https://docs.chain.link/vrf/v2/subscription/supported-networks/#ethereum-mainnet) to see an example of the different gas prices for the different lanes and their associated hashes. - `callbackGasLimit`: Maximum gas for callback function `fulfillRandomWords`. - `requestConfirmations`: Number of block confirmations to wait before the request is returned. - `numWords`: Number of random values to request (just one in this case). - `s_rollers`: Maps VRF request IDs to user addresses. - `s_results`: Maps user addresses to their random result (Hogwarts house ID). #### Events ```solidity event DiceRolled(uint256 indexed requestId, address indexed roller); event DiceLanded(uint256 indexed requestId, uint256 indexed result); ``` - `DiceRolled`: Emitted when randomness is requested. - `DiceLanded`: Emitted when randomness is received. #### Constructor ```solidity constructor(uint256 subscriptionId) VRFConsumerBaseV2Plus(VRF_COORDINATOR) { s_subscriptionId = subscriptionId; } ``` - Initializes the contract with a VRF subscription ID. - Passes the VRF coordinator address to the parent contract. #### Request Randomness Function ```solidity function rollDice() public returns (uint256 requestId) { require(s_results[msg.sender] == 0, "Already rolled"); requestId = s_vrfCoordinator.requestRandomWords( VRFV2PlusClient.RandomWordsRequest({ keyHash: KEY_HASH, subId: s_subscriptionId, requestConfirmations: requestConfirmations, callbackGasLimit: callbackGasLimit, numWords: numWords, extraArgs: VRFV2PlusClient._argsToBytes( VRFV2PlusClient.ExtraArgsV1({nativePayment: false}) ) }) ); s_rollers[requestId] = msg.sender; s_results[msg.sender] = ROLL_IN_PROGRESS; emit DiceRolled(requestId, msg.sender); } ``` - Checks that the caller hasn't already rolled. - Requests a random number from Chainlink VRF. - Records the caller's address in the `s_rollers` mapping, and marks their roll as in progress in the `s_results` mapping. - Emits an event with the request ID and caller's address. **Note**: We have set it to use LINK tokens for payment (`nativePayment`: false). If `nativePayment` was set to `true`, the fees would be paid in the native tokens (e.g. ETH on Ethereum). #### Callback Function ```solidity function fulfillRandomWords( uint256 requestId, uint256[] calldata randomWords ) internal override { uint256 d6Value = (randomWords[0] % 4); s_results[s_rollers[requestId]] = d6Value; emit DiceLanded(requestId, d6Value); } ``` - Called by VRF when the random number (word) is returned. - Takes the random value and converts it to a number between 0-3 (for the four houses) using the modulus operator `%` (remainder after division). - Updates the user's result with their house ID. - Emits an event with the request ID and result. #### House Query Function ```solidity function house(address player) public view returns (string memory) { require(s_results[player] != 0, "Dice not rolled"); require(s_results[player] != ROLL_IN_PROGRESS, "Roll in progress"); return _getHouseName(s_results[player]); } ``` - Returns the house name for a given player's ID. - Requires that the player has completed a roll. - Calls the private helper function to convert house ID to a name. ### House Name Helper ```solidity function _getHouseName(uint256 id) private pure returns (string memory) { string[4] memory houseNames = [ "Gryffindor", // id = 0 "Hufflepuff", // id = 1 "Slytherin", // id = 2 "Ravenclaw" // id = 3 ]; return houseNames[id]; } ``` - Maps house IDs (0-3) to their names - Returns the corresponding house name string ### Compiling and deploying the consumer contract - Compile the contract using the steps detailed in Section 2. - As per the description in Section 2, now connect MetaMask to Remix. - Remember that subscription ID we copied when we created the subscription? Go back to the VRF app page and copy your subscription ID (if you haven't already): 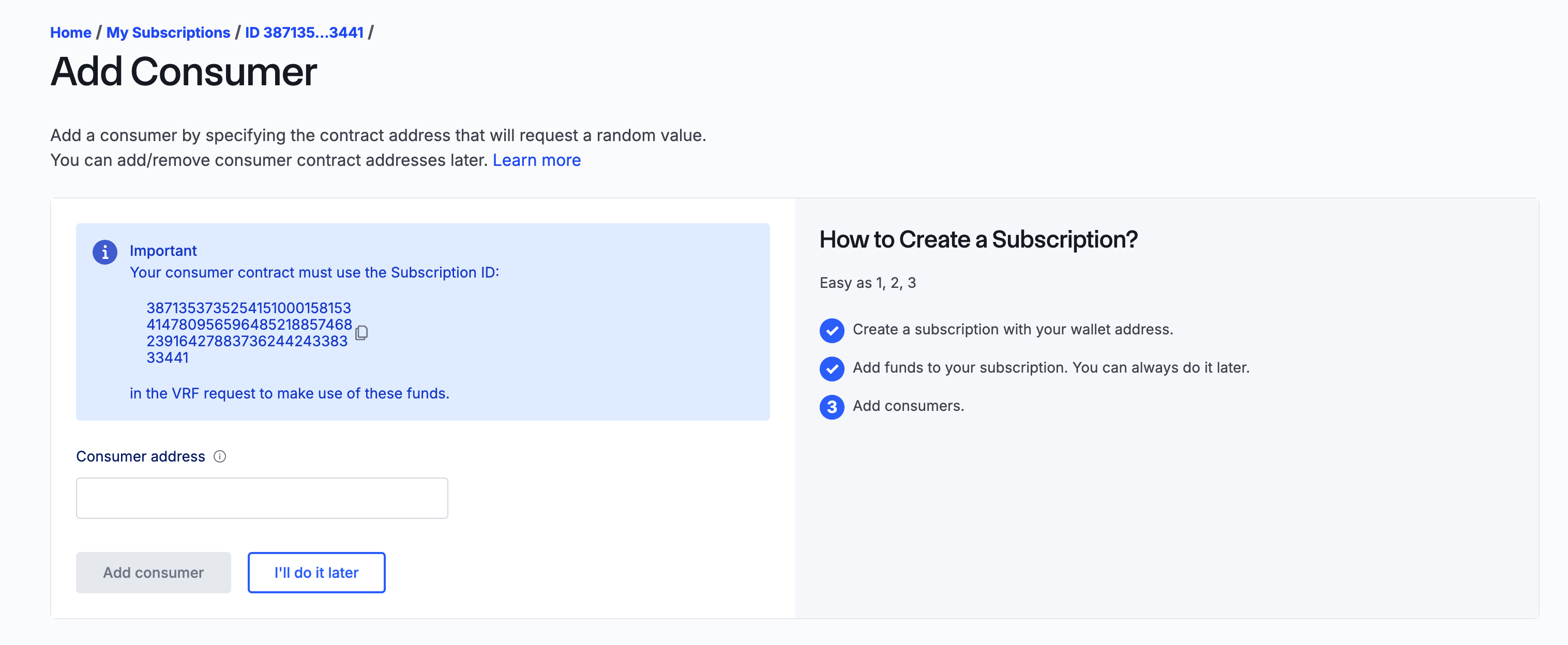 - Paste this as the `subscriptionId` constructor parameter and click **Deploy**: 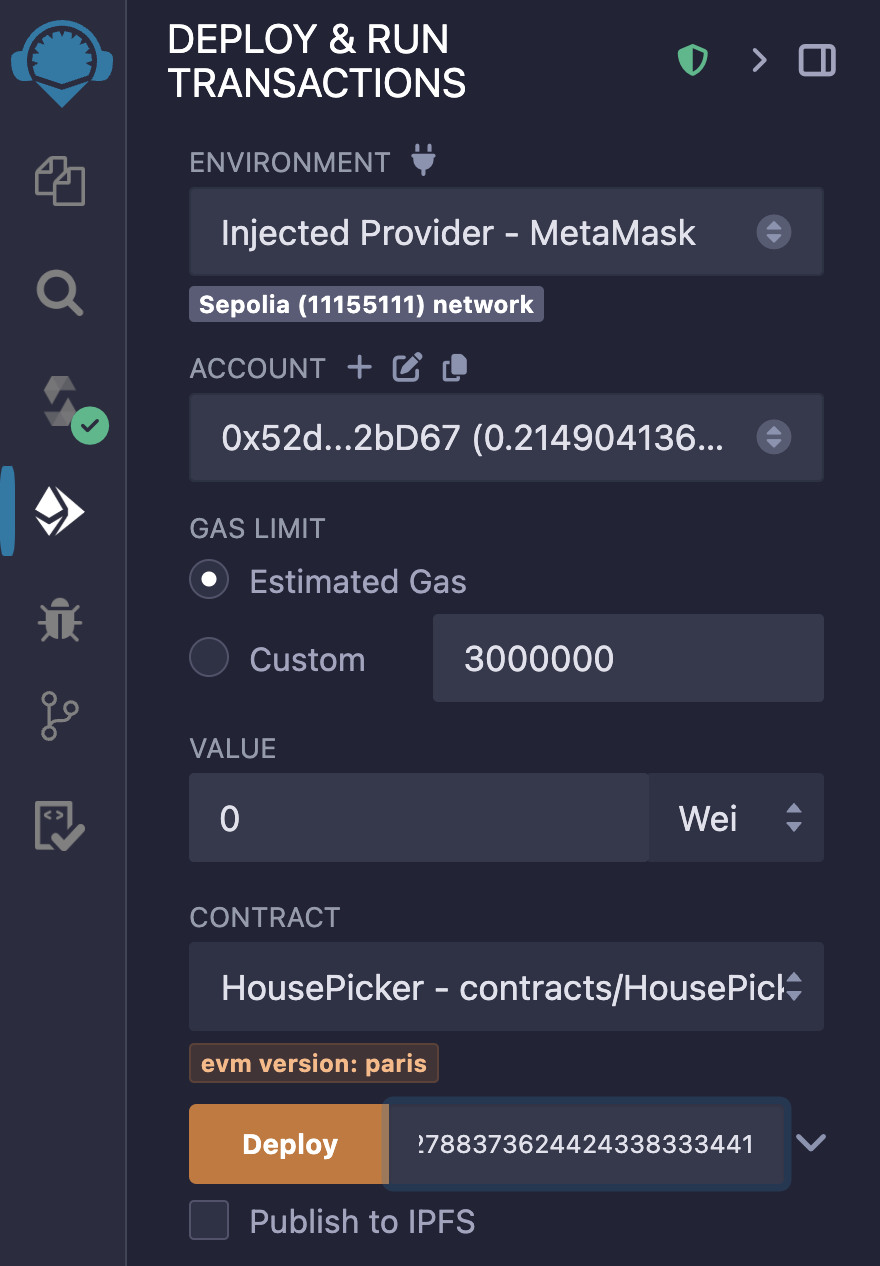 - Remember to pin the contract to your workspace! - Once it has been deployed, you can see and interact with the functions on the contract if you click the contract dropdown in the **Deployed Contracts** section. - Copy the contract address! ### Adding consumer to subscription Let's go back to the VRF app. We have deployed our consumer contract `HousePicker` - let's add it to the subscription. - Paste the contract address of the `HousePicker` contract as the **Consumer address** and click **Add consumer**: 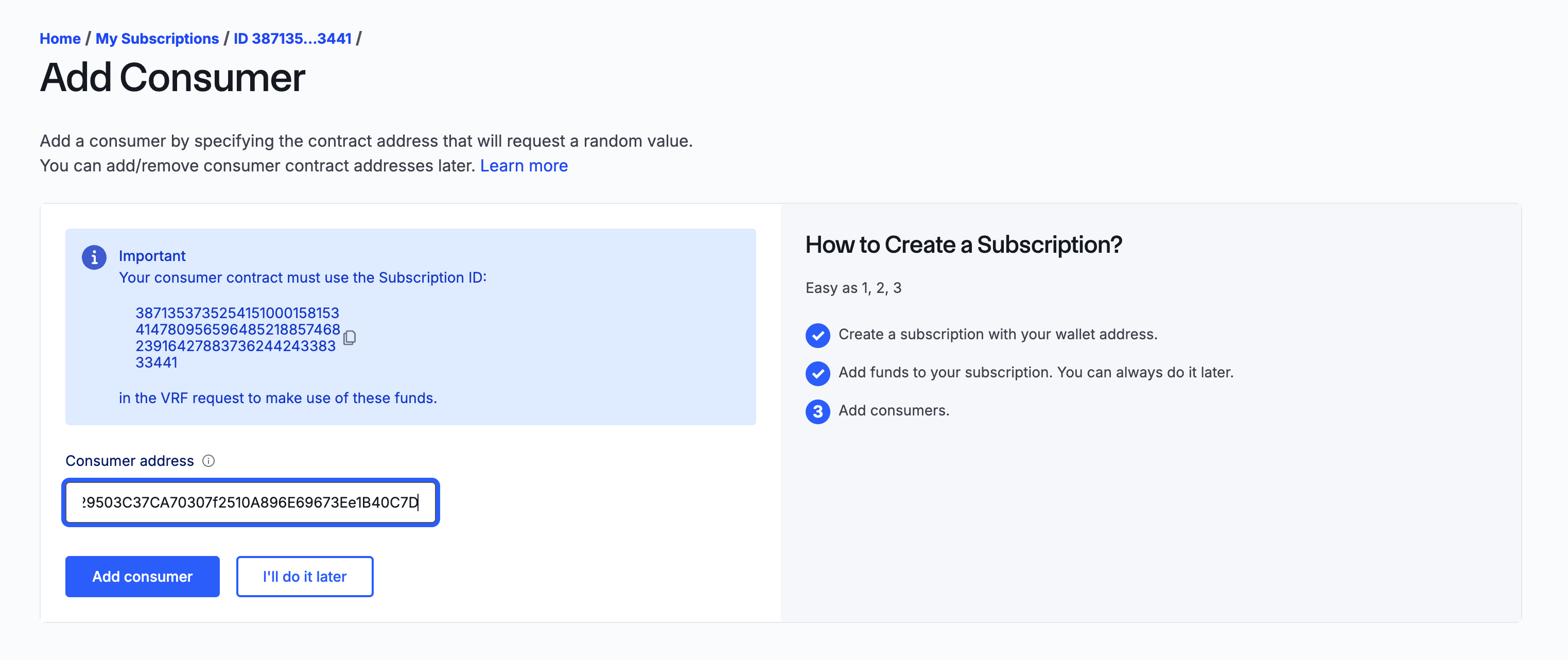 - Sign the transaction to approve adding the consumer to the subscription. - Once the transaction has confirmed, you will be able to view your subscription by clicking the **View subscription** button: 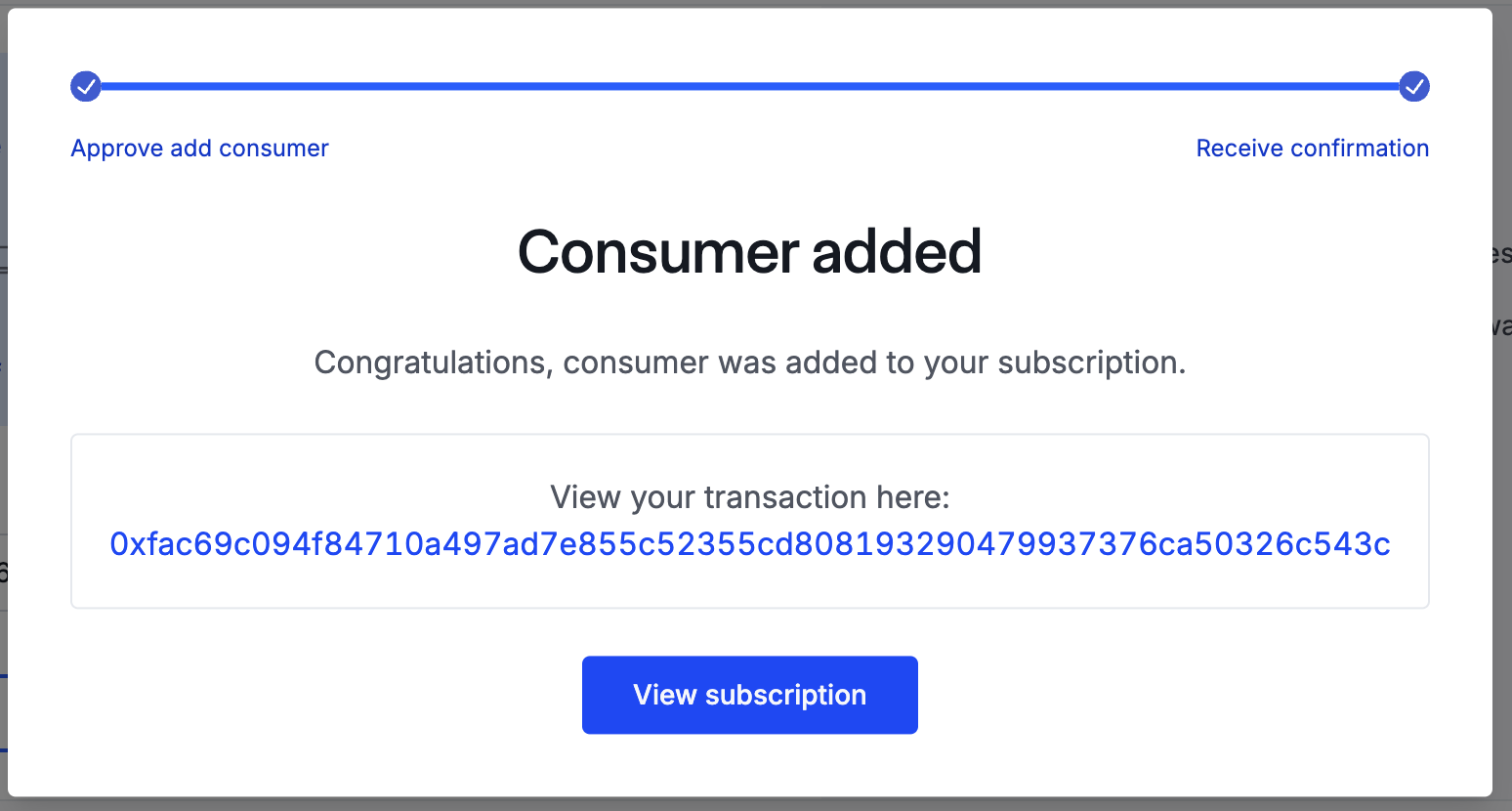 - This will take you to an overview of your active subscriptions; click on the ID of your active subscription to open it: 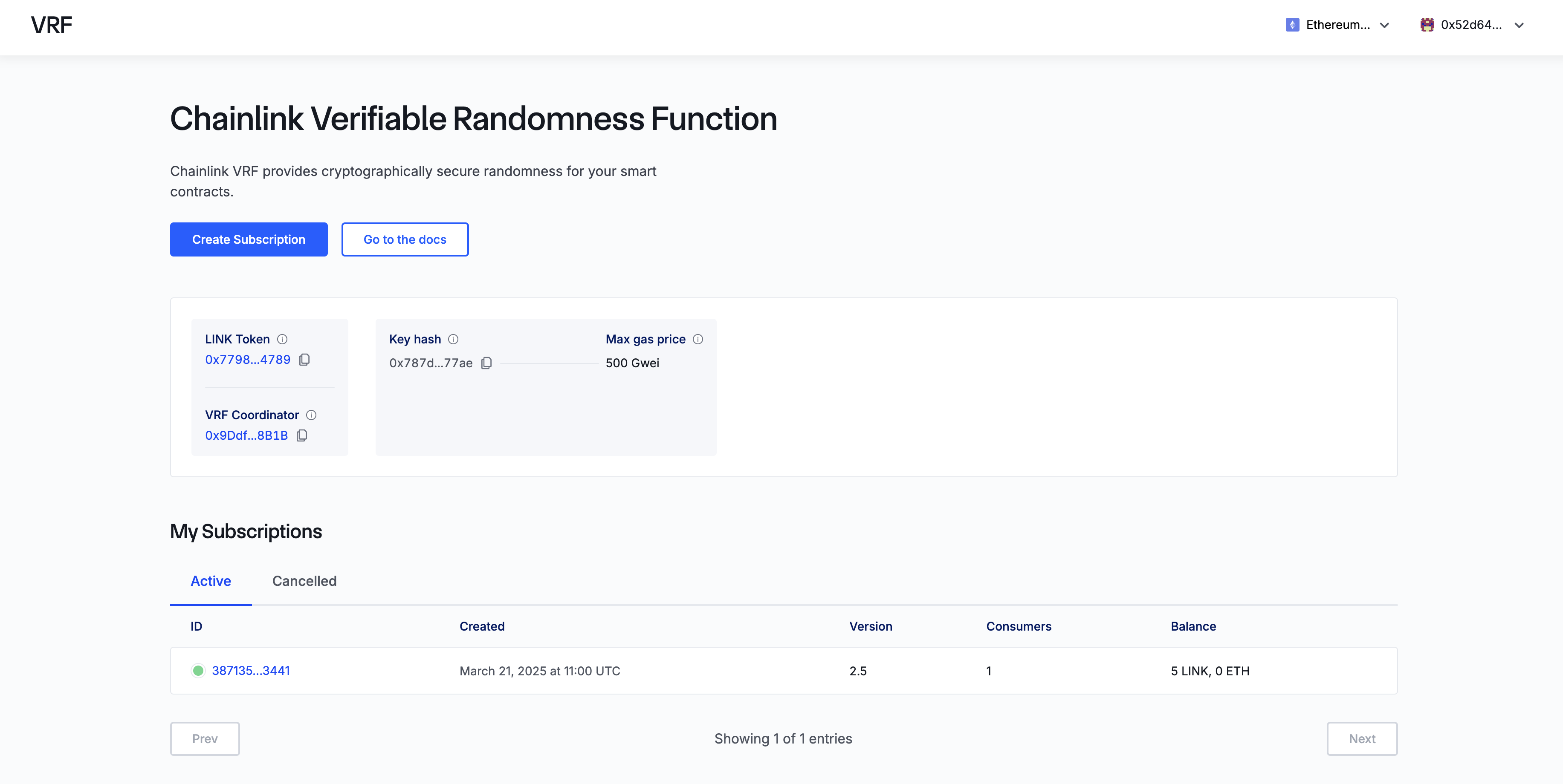 - You will be able to see how many fulfillments have occurred on your subscription and the balance: 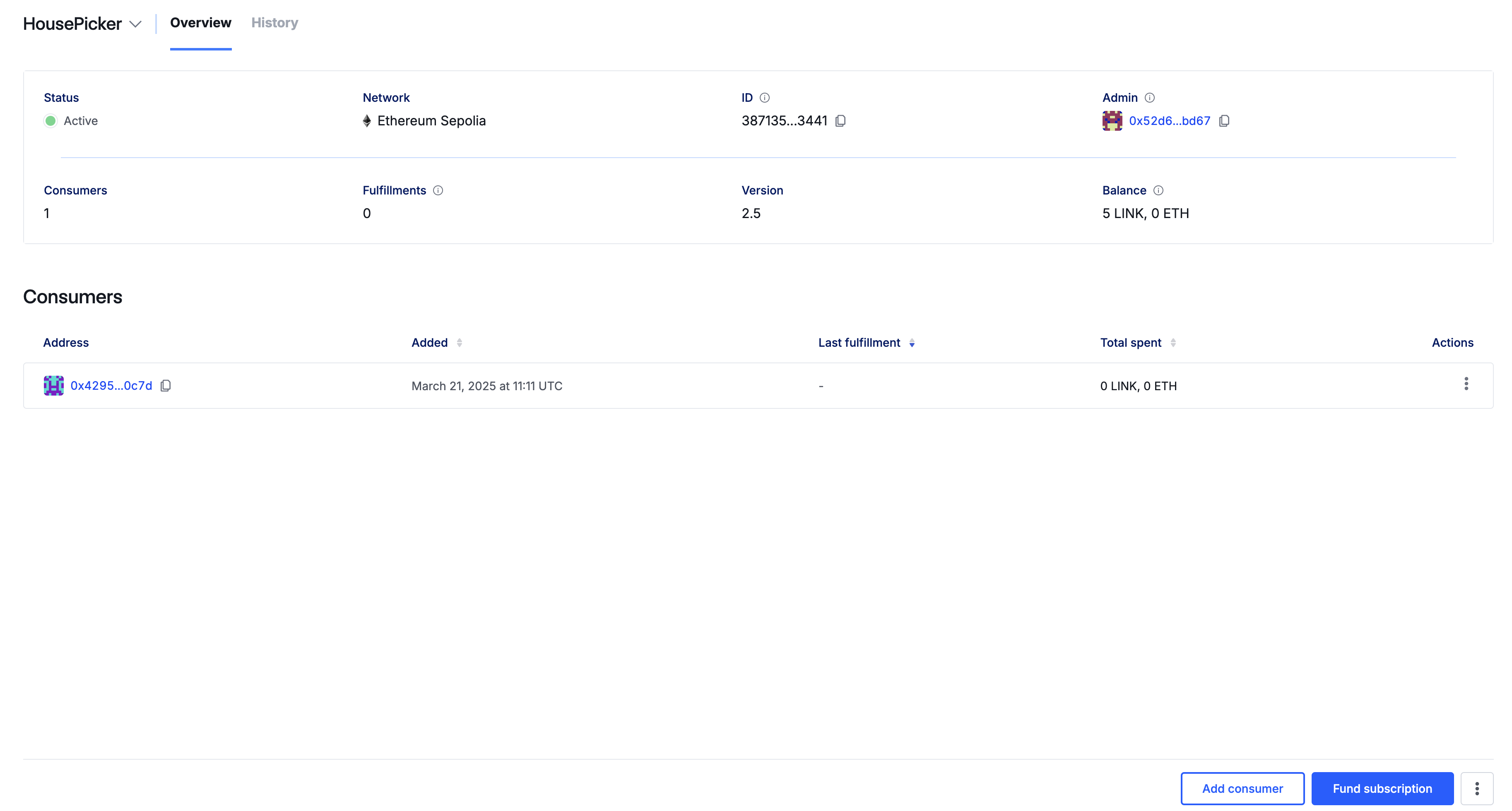 Let's make a request for a random number (this is sometimes referred to as a "request for randomness but means the same thing)! ### Requesting a random number To send a request for a random number and get a Hogwarts house, we need to call `rollDice`. This function will return the `requestId` to see when our request has been fulfilled:  Once you have signed the transaction, you can view the pending request in the Subscription Overview page. This will happen if you do not have enough LINK in the subscription (which I didn't) - you can click the **Fund subscription** button to add extra funds at any time. 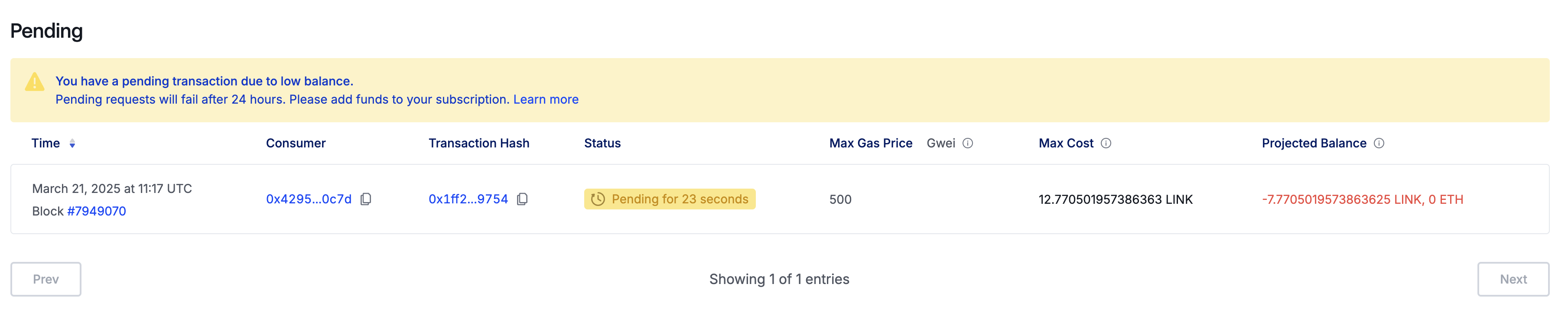 Once your request has been fulfilled, it will be visible in the **History** tab: 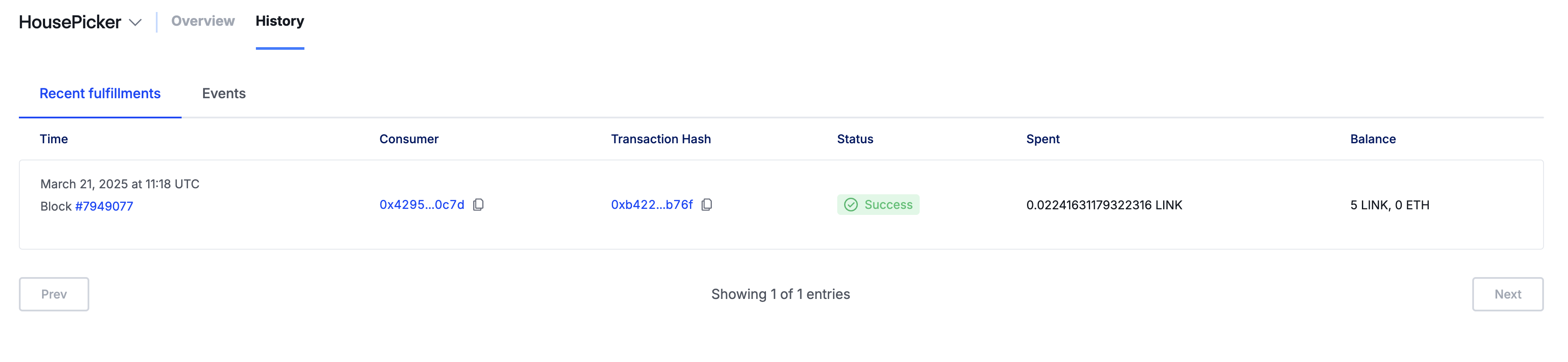 Now, you can go back to your contract in Remix and call `house`, passing your address as an argument, to see which Hogwarts house you were selected for: 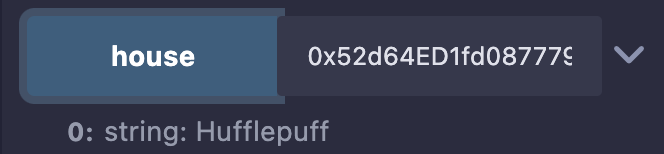 And that's it! You have successfully created a VRF consumer smart contract and used the subscription model to fund requests for randomness.
Chainlink VRF in a Smart Contract
In this lesson, we will write a Chainlink VRF consumer smart contract. This contract is a fun little demo that shows you how to "roll a dice" in a smart contract. This is useful in many gaming applications, but the purpose is to show you how to implement VRF in a smart contract.
Note: as always, if you want to skip the code explanation, it is optional, so please do so and go straight to deploying the contract. If you are a developer (or an aspiring one), I recommend you read through the explanation.
Writing a VRF consumer smart contract
Let's write a smart contract that gets a random number, uses that to mimic rolling a 4 sided die, and then assigns the roll to a Hogwarts House for the roller.
Open Remix and create a new workspace called "VRF", create a folder called contracts and a file called HousePicker.sol inside this folder. In this file, paste the code from the HousePicker.sol file in the course code repo.
Code Walkthrough
Imports
VRFConsumerBaseV2Plus: Abstract contract that VRF consumer contracts need to inherit.VRFV2PlusClient: Library with structs and helpers for VRF requests.
Contract declaration
Inherits from VRFConsumerBaseV2Plus to be VRF compatible.
Constant and state variables
ROLL_IN_PROGRESS: Constant used to track when a roll is being processed. It is auint256that is larger than the highest possible index.s_subscriptionId: The Chainlink VRF subscription ID.VRF_COORDINATOR: Address of the VRF coordinator contract on Sepolia.KEY_HASH: Identifies the VRF gas lane to use. Picking a specific gas lane means picking the maximum gas price you are willing to pay for a request in gwei. Visit the supported networks page to see an example of the different gas prices for the different lanes and their associated hashes.callbackGasLimit: Maximum gas for callback functionfulfillRandomWords.requestConfirmations: Number of block confirmations to wait before the request is returned.numWords: Number of random values to request (just one in this case).s_rollers: Maps VRF request IDs to user addresses.s_results: Maps user addresses to their random result (Hogwarts house ID).
Events
DiceRolled: Emitted when randomness is requested.DiceLanded: Emitted when randomness is received.
Constructor
Initializes the contract with a VRF subscription ID.
Passes the VRF coordinator address to the parent contract.
Request Randomness Function
Checks that the caller hasn't already rolled.
Requests a random number from Chainlink VRF.
Records the caller's address in the
s_rollersmapping, and marks their roll as in progress in thes_resultsmapping.Emits an event with the request ID and caller's address.
Note: We have set it to use LINK tokens for payment (nativePayment: false). If nativePayment was set to true, the fees would be paid in the native tokens (e.g. ETH on Ethereum).
Callback Function
Called by VRF when the random number (word) is returned.
Takes the random value and converts it to a number between 0-3 (for the four houses) using the modulus operator
%(remainder after division).Updates the user's result with their house ID.
Emits an event with the request ID and result.
House Query Function
Returns the house name for a given player's ID.
Requires that the player has completed a roll.
Calls the private helper function to convert house ID to a name.
House Name Helper
Maps house IDs (0-3) to their names
Returns the corresponding house name string
Compiling and deploying the consumer contract
Compile the contract using the steps detailed in Section 2.
As per the description in Section 2, now connect MetaMask to Remix.
Remember that subscription ID we copied when we created the subscription? Go back to the VRF app page and copy your subscription ID (if you haven't already):

Paste this as the
subscriptionIdconstructor parameter and click Deploy:

-
Remember to pin the contract to your workspace!
-
Once it has been deployed, you can see and interact with the functions on the contract if you click the contract dropdown in the Deployed Contracts section.
-
Copy the contract address!
Adding consumer to subscription
Let's go back to the VRF app. We have deployed our consumer contract HousePicker - let's add it to the subscription.
Paste the contract address of the
HousePickercontract as the Consumer address and click Add consumer:

Sign the transaction to approve adding the consumer to the subscription.
Once the transaction has confirmed, you will be able to view your subscription by clicking the View subscription button:

This will take you to an overview of your active subscriptions; click on the ID of your active subscription to open it:

You will be able to see how many fulfillments have occurred on your subscription and the balance:

Let's make a request for a random number (this is sometimes referred to as a "request for randomness but means the same thing)!
Requesting a random number
To send a request for a random number and get a Hogwarts house, we need to call rollDice.
This function will return the requestId to see when our request has been fulfilled:

Once you have signed the transaction, you can view the pending request in the Subscription Overview page. This will happen if you do not have enough LINK in the subscription (which I didn't) - you can click the Fund subscription button to add extra funds at any time.

Once your request has been fulfilled, it will be visible in the History tab:

Now, you can go back to your contract in Remix and call house, passing your address as an argument, to see which Hogwarts house you were selected for:

And that's it! You have successfully created a VRF consumer smart contract and used the subscription model to fund requests for randomness.
VRF In A Smart Contract
A hands-on implementation of Chainlink VRF in a Smart Contract - Walk through building a `HousePicker` contract that requests verifiable randomness using `VRFConsumerBaseV2Plus`. Covers deployment, subscription management, and handling the random number callback.
Previous lesson
Previous
Next lesson
Next
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Smart contract and Solidity fundamentals
Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network (DON)
Chainlink Data Feeds
Chainlink Data Streams
Chainlink Automation
Chainlink CCIP
Chainlink Functions
Verifiable Random Function (VRF)
Chainlink Proof of Reserve
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Smart Contract Developers
- Solutions Architects
- Blockchain Engineers
- Web3 Developers
- Security Researchers
Potential Careers
Smart Contract Engineer
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
DeFi Developer
$75,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 developer
$60,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 Developer Relations
$85,000 - $125,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Blockchain Financial Analyst
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Last updated on July 25, 2025
Duration: 9min
Duration: 1h 17min
Duration: 42min
Duration: 30min
Duration: 1h 03min
Duration: 49min
Duration: 30min
Duration: 19min
Duration: 37min
Duration: 30min
Certification: Chainlink Fundamentals
The Chainlink Fundamentals proficiency exam covers is designed to confirm your grasp of all key concepts and learnings presented in the course material. Exam takers will have 75 minutes to complete 50 questions and must score 30/50 to pass and earn a Certificate of Completion. Because course material is continually updated, The Chainlink Fundamentals Certificate of Completions expires after 1 year. To remain current, holders must re-take the exam and pass to confirm their current knowledge.
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Smart contract and Solidity fundamentals
Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network (DON)
Chainlink Data Feeds
Chainlink Data Streams
Chainlink Automation
Chainlink CCIP
Chainlink Functions
Verifiable Random Function (VRF)
Chainlink Proof of Reserve
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Smart Contract Developers
- Solutions Architects
- Blockchain Engineers
- Web3 Developers
- Security Researchers
Potential Careers
Smart Contract Engineer
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
DeFi Developer
$75,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 developer
$60,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 Developer Relations
$85,000 - $125,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Blockchain Financial Analyst
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Last updated on July 25, 2025

