5/5
_Follow along the course with this video._ --- ### UUPS Tests In this lesson we're going to be writing our test suite which will enable us to really demonstrate how this upgradeability works in practice. Begin by creating the file `test/DeployAndUpgradeTest.t.sol`. We know the drill in setting this up by now! ```solidity // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.18; import {Test} from "forge-std/Test.sol"; import {DeployBox} from "../script/DeployBox.s.sol"; import {UpgradeBox} from "../script/UpgradeBox.s.sol"; import {BoxV1} from "../src/BoxV1.sol"; import {BoxV2} from "../src/BoxV2.sol"; contract DeployAndUpgradeTest is Test { DeployBox public deployer; UpgradeBox public upgrader; address public OWNER = makeAddr("owner"); address public proxy; function setUp(){ deployer = new DeployBox(); upgrader = new UpgradeBox(); proxy = deployer.run(); // currently points to BoxV1 } } ``` This is a little more than boilerplate, but I trust your skills to be improving as we continue, so walking through each step granularly shouldn't be as necessary. In the above, we're simply importing many of the contracts we expect to be working with in our tests and then declaring and deploying them within our setUp function. Now we can write our test, we'll need to deploy BoxV2. ```solidity function testUpgrades() public { BoxV2 box2 = new BoxV2(); upgrader.upgradeBox(proxy, address(box2)); } ``` Recall what our upgradeBox function is going within UpgradeBox.s.sol: ```solidity function upgradeBox(address proxyAddress, address newBox) public returns (address) { vm.startBroadcast(); BoxV1 proxy = BoxV1(proxyAddress); proxy.upgradeTo(address(newBox)); vm.stopBroadcast(); return address(proxy); } ``` This function is taking the proxy address and our new implementation address as parameters and calling the upgradeTo function. Now, in our test, we can set an expected value and compare it against what version a call to the `version` function on our proxy will return. ```solidity function testUpgrades() public { BoxV2 box2 = new BoxV2(); upgrader.upgradeBox(proxy, address(box2)); uint256 expectedValue = 2; assertEq(expectedValue, BoxV2(proxy).version()); } ``` It's best practice to split tests up as best one can, but let's check more here while we're at it. We added new function to BoxV2, let's ensure they work after our upgrade. ```solidity function testUpgrades() public { BoxV2 box2 = new BoxV2(); upgrader.upgradeBox(proxy, address(box2)); uint256 expectedValue = 2; assertEq(expectedValue, BoxV2(proxy).version()); BoxV2(proxy).setNumber(7); assertEq(7, BoxV2(proxy).getNumber()); } ``` You know what, I changed my mind, let's add one more simple test to verify the implementation we begin with. ```solidity function testProxyStartAsBoxV1() public { vm.expectRevert(); BoxV2(proxy).setNumber(7); } ``` We would expect the above to revert because BoxV1, on deployment, doesn't contain a setNumber function! Let's test these one at a time. ```bash forge test --mt testProxyStartAsBoxV1 ``` We would expect this to pass if it reverts. 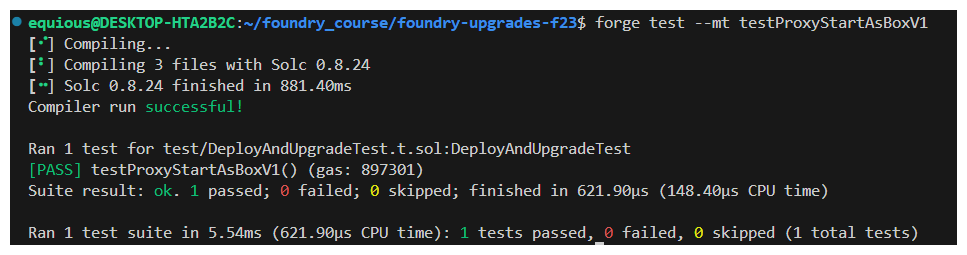 Looks great! Our BoxV1 doesn't have the setNumber function. Now we can try our other test! ```bash forge test --mt testUpgrades ```  ### Wrap Up Boom! We've successfully upgraded our upgradeable Box Protocol. I've included additional tests for this within the [**GitHub Repo**](https://github.com/Cyfrin/foundry-upgrades-f23) for this section, so don't hesitate to try and write your own and compare what you come up with versus the repo! In this section we'll be walking through one big example test, but I encourage you to try to write more, as always.
Follow along the course with this video.
UUPS Tests
In this lesson we're going to be writing our test suite which will enable us to really demonstrate how this upgradeability works in practice.
Begin by creating the file test/DeployAndUpgradeTest.t.sol. We know the drill in setting this up by now!
This is a little more than boilerplate, but I trust your skills to be improving as we continue, so walking through each step granularly shouldn't be as necessary. In the above, we're simply importing many of the contracts we expect to be working with in our tests and then declaring and deploying them within our setUp function.
Now we can write our test, we'll need to deploy BoxV2.
Recall what our upgradeBox function is going within UpgradeBox.s.sol:
This function is taking the proxy address and our new implementation address as parameters and calling the upgradeTo function.
Now, in our test, we can set an expected value and compare it against what version a call to the version function on our proxy will return.
It's best practice to split tests up as best one can, but let's check more here while we're at it. We added new function to BoxV2, let's ensure they work after our upgrade.
You know what, I changed my mind, let's add one more simple test to verify the implementation we begin with.
We would expect the above to revert because BoxV1, on deployment, doesn't contain a setNumber function! Let's test these one at a time.
We would expect this to pass if it reverts.

Looks great! Our BoxV1 doesn't have the setNumber function. Now we can try our other test!

Wrap Up
Boom! We've successfully upgraded our upgradeable Box Protocol.
I've included additional tests for this within the GitHub Repo for this section, so don't hesitate to try and write your own and compare what you come up with versus the repo!
In this section we'll be walking through one big example test, but I encourage you to try to write more, as always.
Testing UUPS Proxies
A detailed guide to Testing UUPS Upgradeable Smart Contracts with Foundry - Explore how to leverage Foundry's testing capabilities (`forge test`) to deploy and thoroughly test UUPS upgradeable contracts. Cover deploying V1 via proxy, performing the upgrade to V2, and verifying interactions and state through the proxy pre- and post-upgrade.
Previous lesson
Previous
Next lesson
Next
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Advanced smart contract development
How to develop a stablecoin
How to develop a DeFi protocol
How to develop a DAO
Advanced smart contracts testing
Fuzz testing
Manual verification
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Engineers
- Smart Contract Security researchers
Potential Careers
Web3 Developer Relations
$85,000 - $125,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 developer
$60,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Engineer
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Meet your instructors
Web3 engineer, educator, and Cyfrin co-founder. Patrick's smart contract development and security courses have helped hundreds of thousands of engineers kickstarting their careers into web3.
Guest lecturers:
Last updated on February 17, 2026
Duration: 37min
Duration: 3h 06min
Duration: 5h 03min
Duration: 6h 22min
Duration: 2h 48min
Duration: 1h 24min
Duration: 4h 28min
Duration: 1h 20min
Duration: 1h 11min
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Advanced smart contract development
How to develop a stablecoin
How to develop a DeFi protocol
How to develop a DAO
Advanced smart contracts testing
Fuzz testing
Manual verification
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Engineers
- Smart Contract Security researchers
Potential Careers
Web3 Developer Relations
$85,000 - $125,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 developer
$60,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Engineer
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Meet your instructors
Web3 engineer, educator, and Cyfrin co-founder. Patrick's smart contract development and security courses have helped hundreds of thousands of engineers kickstarting their careers into web3.
Guest lecturers:
Last updated on February 17, 2026