# Chainlink Data Streams - Streams Trade This project uses the **Streams Trade** implementation of Chainlink Data Streams. This implementation uses Chainlink Automation **Log Trigger** to monitor for an event emission, signaling that data needs to be fetched off-chain. ### Please Note: This section follows a guide in the Chainlink Docs [Access Data Streams Using Automation](https://docs.chain.link/chainlink-automation/guides/streams-lookup). This service is restricted to those who [gain access](https://chainlinkcommunity.typeform.com/datastreams?typeform-source=docs.chain.link#ref_id=docs) to Data Streams from the Chainlink team. Therefore, it is unlikely that you will be able to reproduce this section of the course, but you can still read our guide and see how Data Streams are used! ## How does the Streams Trade implementation work? 1. An event is emitted from an emitter smart contract, which we will write and name `LogEmitter`. 2. We will tell Automation to call a second contract when this event is emitted. When Automation detects the event has been emitted, it runs the **`checkLog`** function implemented on the second smart contract which we will write and name `StreamsUpkeep`. `checkLog` and will return a [StreamsLookup custom error](https://docs.chain.link/chainlink-automation/reference/automation-interfaces#streamslookup-revert). Don't worry too much about this right now, we will go through this again as we write the code. 3. Chainlink Automation uses the **`StreamsLookup`** custom error to retrieve a signed report from the Data Streams Aggregation Network and return the data in a callback to the `performUpkeep` function. 4. The **`performUpkeep`** function verifies the data by calling the **`verify`** function on the Chainlink Verifier contract. 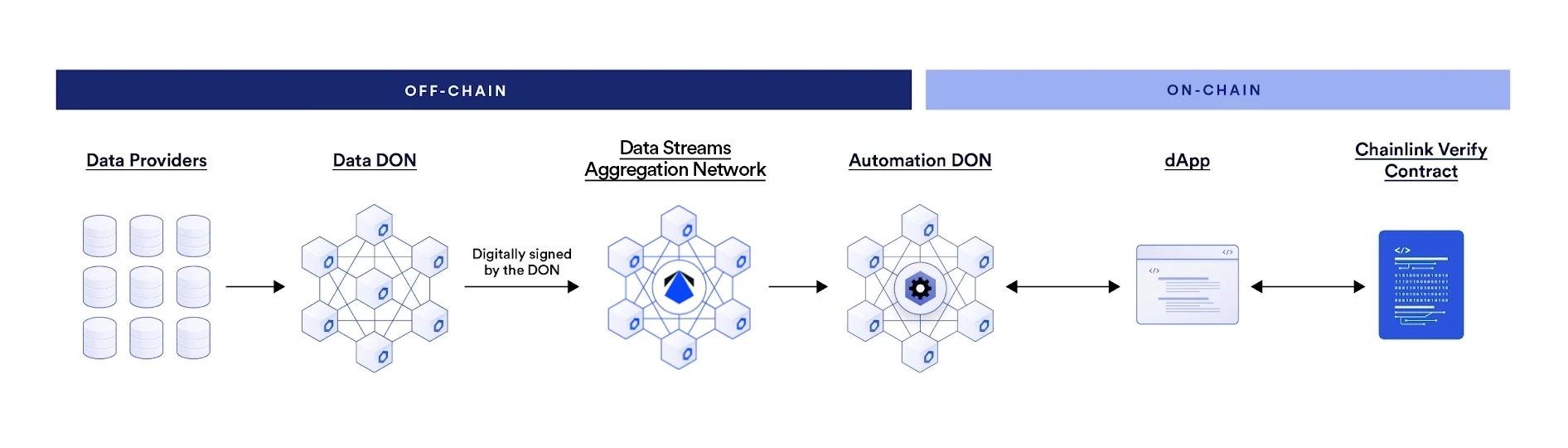 ## Writing the code We are going to write two smart contracts: 1. A `LogEmitter` contract. This is a simple, smart contract with a single function that emits an event. Automation will pick up this Event to trigger the retrieval of the off-chain data. This function is a simple example in place of an action that a user would perform, such as minting, staking, borrowing, etc. 2. A `StreamsUpkeep` contract. This contract will contain the Automation logic, including: - Callback for data processing. - Callback for error processing. - `performUpkeep` function for Automation to return the data. - We will request the ETH/USD price stream. ### 1. LogEmitter contract First, let’s create a smart contract that emits the event that will trigger Automation to perform an upkeep and retrieve the data from the ETH/USD data stream. Usually, this would be a part of a dApp, and this event would be triggered when a user performs an action such as initiating a trade. We are going to keep this simple. - Create a new workspace called "Data Streams". Make a folder called `contracts` and a file called `LogEmitter.sol` - Create a simple, smart contract with a function called `emitLog` that simply emits an event with the caller address as an indexed parameter. - Copy and paste the code from the `LogEmitter.sol` contract in the [course code repo](https://github.com/ciaranightingale/chainlink-fundamentals-code/blob/main/data-streams/LogEmitter.sol). ### 2. StreamsUpkeep contract Now, let’s write our upkeep smart contract, which Automation will call when `LogEmitter::emitLog` is called. - Create a file called `StreamsUpkeep.sol` in the `contracts` folder. In this file, copy and paste the code from the `StreamsUpkeep.sol` contract in the [course code repo](https://github.com/Cyfrin/chainlink-fundamentals-cu/blob/main/chainlink-course-code/data-streams/StreamsUpkeep.sol). **Note**: as of writing, `@chainlink v1.3.0` requires you use a compiler version of `0.8.19`. #### Interfaces This contract is going to interact with two smart contracts which we need to add interfaces for so that we can call their functions: 1. The `FeeManager`: allows our smart contract to get the fees for performing the verification 2. The `VerifierProxy`: this smart contract is responsible for performing the verification of the streams data and also stores the address of the `FeeManager` contract - Add a folder called `interfaces` inside your `contracts` folder, add a file called `IFeeManager.sol`, and add the following interface from the [course code repo](https://github.com/ciaranightingale/chainlink-fundamentals-code/blob/main/data-streams/interfaces/IFeeManager.sol). This is the interface the `FeeManager` will need to conform to which allows callers to get the data streams fees. - Then, create a file called `IVerifierProxy.sol`, again inside that interfaces folder, and add the following interface from the [course code repo](https://github.com/ciaranightingale/chainlink-fundamentals-code/blob/main/data-streams/interfaces/IVerifierProxy.sol). This is the interface the `VerifierProxy` contract will conform to. It allows callers to verify the returned signed data. ### Code walkthrough Let’s now walk through the `StreamsUpkeep` code so we know what’s happening. As always, this section is optional and targeted toward those who want to understand how to implement Data Streams. Feel free to skip to the deployment section. #### Imports ```solidity import {Common} from "@chainlink/contracts@1.3.0/src/v0.8/llo-feeds/libraries/Common.sol"; import {StreamsLookupCompatibleInterface} from "@chainlink/contracts@1.3.0/src/v0.8/automation/interfaces/StreamsLookupCompatibleInterface.sol"; import {ILogAutomation, Log} from "@chainlink/contracts@1.3.0/src/v0.8/automation/interfaces/ILogAutomation.sol"; import {IRewardManager} from "@chainlink/contracts@1.3.0/src/v0.8/llo-feeds/v0.3.0/interfaces/IRewardManager.sol"; import {IERC20} from "@chainlink/contracts@1.3.0/src/v0.8/vendor/openzeppelin-solidity/v4.8.3/contracts/interfaces/IERC20.sol"; import {IFeeManager} from "./interfaces/IFeeManager.sol"; import {IVerifierProxy} from "./interfaces/IVerifierProxy.sol"; ``` Imports several Chainlink-specific interfaces: - `Common`: Utilities for working with Chainlink Low Latency Oracle (LLO) feeds - `StreamsLookupCompatibleInterface`: Interface for contracts that work with Streams Lookup - `ILogAutomation`: Interface for log-triggered automation - `IRewardManager`: Interface for managing rewards in the Chainlink ecosystem - `IERC20`: Standard ERC20 interface for token interactions - The custom interfaces we just created #### Contract declaration ```solidity contract StreamsUpkeep is ILogAutomation, StreamsLookupCompatibleInterface {} ``` - Inherits from two interfaces to be enabled for Chainlink Automation and Data Streams. #### Error definition ```solidity error InvalidReportVersion(uint16 version); ``` - Defines a custom error for handling unsupported report versions #### V3 and V4 Reports Chainlink Data Streams organize reports in two different standardized formats: the V3 format (used for cryptocurrency assets) and the V4 format (used for real-world assets). Each report format defines a specific set of data fields that contain the price information and related details, as shown in these Solidity structs: ```solidity struct ReportV3 { bytes32 feedId; // The stream ID the report has data for. uint32 validFromTimestamp; // Earliest timestamp for which price is applicable. uint32 observationsTimestamp; // Latest timestamp for which price is applicable. uint192 nativeFee; // Base cost to validate a transaction using the report, denominated in the chain’s native token (e.g., WETH/ETH). uint192 linkFee; // Base cost to validate a transaction using the report, denominated in LINK. uint32 expiresAt; // Latest timestamp where the report can be verified on-chain. int192 price; // DON consensus median price (8 or 18 decimals). int192 bid; // Simulated price impact of a buy order up to the X% depth of liquidity utilization (8 or 18 decimals). int192 ask; // Simulated price impact of a sell order up to the X% depth of liquidity utilization (8 or 18 decimals). } /** * @dev Represents a data report from a Data Streams stream for v4 schema (RWA streams). * The `price` value is carried to 8 or 18 decimal places, depending on the stream. * The `marketStatus` indicates whether the market is currently open. Possible values: `0` (`Unknown`), `1` (`Closed`), `2` (`Open`). * For more information, see https://docs.chain.link/data-streams/rwa-streams and https://docs.chain.link/data-streams/reference/report-schema-v4 */ struct ReportV4 { bytes32 feedId; // The stream ID the report has data for. uint32 validFromTimestamp; // Earliest timestamp for which price is applicable. uint32 observationsTimestamp; // Latest timestamp for which price is applicable. uint192 nativeFee; // Base cost to validate a transaction using the report, denominated in the chain’s native token (e.g., WETH/ETH). uint192 linkFee; // Base cost to validate a transaction using the report, denominated in LINK. uint32 expiresAt; // Latest timestamp where the report can be verified on-chain. int192 price; // DON consensus median benchmark price (8 or 18 decimals). uint32 marketStatus; // The DON's consensus on whether the market is currently open. } ``` #### Quote struct ```solidity struct Quote { address quoteAddress; } ``` A simple structure to hold token addresses for fee quotes #### State variables - There are a few constant variables we need: - `DATASTREAMS_FEEDLABEL`: This is the first parameter passed to the `StreamsLookup` custom error revert. We will explain the custom error shortly, but `DATASTREAMS_FEEDLABEL` is a string that specifies the feed IDs that will be provided. The only allowed value is **`"feedIDs"`** - `DATASTREAMS_QUERYLABEL`: This is the third parameter passed to the `StreamsLookup` custom error called `timeParamKey`. The only allowed value is **`“timestamp”`.** - `VERIFIER`: the address of the [Chainlink verifier](https://docs.chain.link/data-streams/crypto-streams?page=1#streams-verifier-network-addresses)(there is one verifier contract deployed on all available chains) on the specific chain you are working on. - Additionally, we need to save the `feedIds` in a string array state variable. This is the ID for the specific stream (e.g., for `ETH/USD` the ID is `"0x000359843a543ee2fe414dc14c7e7920ef10f4372990b79d6361cdc0dd1ba782"` on testnet). - The full list of verifier addresses and feed IDs can be found in the Chainlink documentation: - [Cryptocurrency streams](https://docs.chain.link/data-streams/crypto-streams?page=1) - [Real world asset streams](https://docs.chain.link/data-streams/rwa-streams?page=1) ```solidity IVerifierProxy public VERIFIER = IVerifierProxy(0x4e9935be37302B9C97Ff4ae6868F1b566ade26d2); string public constant DATASTREAMS_FEEDLABEL = "feedIDs"; string public constant DATASTREAMS_QUERYLABEL = "timestamp"; int192 public lastDecodedPrice; // This example reads the ID for the ETH/USD report. // Find a complete list of IDs at https://docs.chain.link/data-streams/crypto-streams. string[] public feedIds = [ "0x000359843a543ee2fe414dc14c7e7920ef10f4372990b79d6361cdc0dd1ba782" ]; ``` #### checkLog function ```solidity // This function uses revert to convey call information. // See https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-3668#rationale for details. function checkLog( Log calldata log, bytes memory ) external returns (bool upkeepNeeded, bytes memory performData) { revert StreamsLookup( DATASTREAMS_FEEDLABEL, // Specify the feed identifiers that will be provided feedIds, // String list of feed identifiers DATASTREAMS_QUERYLABEL, // Specify query type log.timestamp, // Specify query value "" // Any extra data user wants to receive in callback, alongside API bytes[] ); } ``` The `checkLog` function is the function called by Automation when it detects the event emission. The code example uses `revert` with the `StreamsLookup` custom error to convey all the information about what stream(s) to retrieve. This use of `revert` is part of the [EIP-3668](https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-3668#rationale) specification, which proposes that contracts revert with specific data to indicate that off-chain data is needed. The revert message contains information needed for off-chain lookups. It intentionally reverts with a special error that contains: - ID of the feed to fetch data from. - A timestamp for context. Chainlink nodes catch this revert and use it to fetch data from Data Streams. More information on EIP-3668 can be found at the end of this lesson. #### checkCallback function ```solidity // The Data Streams report bytes is passed here. // extraData is context data from stream lookup process. // Your contract may include logic to further process this data. // This method is intended only to be simulated offchain by Automation. // The data returned will then be passed by Automation into performUpkeep function checkCallback( bytes[] calldata values, bytes calldata extraData ) external pure returns (bool, bytes memory) { return (true, abi.encode(values, extraData)); } ``` The following function is a callback function (which is simulated off-chain, hence why it is `pure`), so it can be modified to further process the report data. The report and data are then passed into `performUpkeep` by Automation. #### performUpkeep function ```solidity // function will be performed onchain function performUpkeep(bytes calldata performData) external { // Decode the performData bytes passed in by CL Automation. // This contains the data returned by your implementation in checkCallback(). (bytes[] memory signedReports, ) = abi.decode( performData, (bytes[], bytes) ); bytes memory unverifiedReport = signedReports[0]; (, /* bytes32[3] reportContextData */ bytes memory reportData) = abi .decode(unverifiedReport, (bytes32[3], bytes)); // Extract report version from reportData uint16 reportVersion = (uint16(uint8(reportData[0])) << 8) | uint16(uint8(reportData[1])); // Validate report version if (reportVersion != 3 && reportVersion != 4) { revert InvalidReportVersion(uint8(reportVersion)); } // Report verification fees IFeeManager feeManager = IFeeManager(address(VERIFIER.s_feeManager())); IRewardManager rewardManager = IRewardManager( address(feeManager.i_rewardManager()) ); address feeTokenAddress = feeManager.i_linkAddress(); (Common.Asset memory fee, , ) = feeManager.getFeeAndReward( address(this), reportData, feeTokenAddress ); // Approve rewardManager to spend this contract's balance in fees IERC20(feeTokenAddress).approve(address(rewardManager), fee.amount); // Verify the report bytes memory verifiedReportData = VERIFIER.verify( unverifiedReport, abi.encode(feeTokenAddress) ); // Decode verified report data into the appropriate Report struct based on reportVersion if (reportVersion == 3) { // v3 report schema ReportV3 memory verifiedReport = abi.decode( verifiedReportData, (ReportV3) ); // Store the price from the report lastDecodedPrice = verifiedReport.price; } else if (reportVersion == 4) { // v4 report schema ReportV4 memory verifiedReport = abi.decode( verifiedReportData, (ReportV4) ); // Store the price from the report lastDecodedPrice = verifiedReport.price; } } ``` `performUpkeep` is the function that is executed on-chain by Automation. It contains the logic to process the data and record it on-chain. In this function, we are simply: - Decoding the `performData` - Extracting the report - Validating the report version - Approving the fees to be paid - Verifying the report - Decoding the report into the relevant struct (V3 or V4) - Storing the report data in a state variable `lastDecodedPrice`. #### checkErrorHandler function Finally, the `checkErrorHandler` function is included to show you how you can implement logic into this function to surface any errors. In this example, we have kept things simple and hardcoded it to return `true` for `upkeepNeeded` (aka, always fetch a report) and not pass any `performData`: ```solidity /** * @notice this is a new, optional function in streams lookup. It is meant to surface streams lookup errors. * @return upkeepNeeded boolean to indicate whether the keeper should call performUpkeep or not. * @return performData bytes that the keeper should call performUpkeep with, if * upkeep is needed. If you would like to encode data to decode later, use `abi.encode`. */ function checkErrorHandler( uint256 /*errCode*/, bytes memory /*extraData*/ ) external pure returns (bool upkeepNeeded, bytes memory performData) { return (true, "0"); // Hardcoded to always perform upkeep. // Read the StreamsLookup error handler guide for more information. // https://docs.chain.link/chainlink-automation/guides/streams-lookup-error-handler } ``` ## Compile and deploy the contracts Compile and deploy both the `StreamsUpkeep` and `LogEmitter` contracts to Sepolia using the steps detailed in Section 2. Make sure you pin both contracts to your workspace. ### Fund the StreamsUpkeep with LINK To pay for Automation, we need to fund our `StreamsUpkeep` contract with LINK. In Metamask, click the LINK token in the **Tokens** tab, then click the **Send** button. Send `1 LINK` to the `StreamsUpkeep` address (that you just deployed). - Enter the contract address of the StreamUpkeep contract as the **To** address (you can copy the address in Remix) - Enter the amount as `1`. Click **Continue** and then sign the transaction by clicking **Confirm** to fund the contract with LINK. 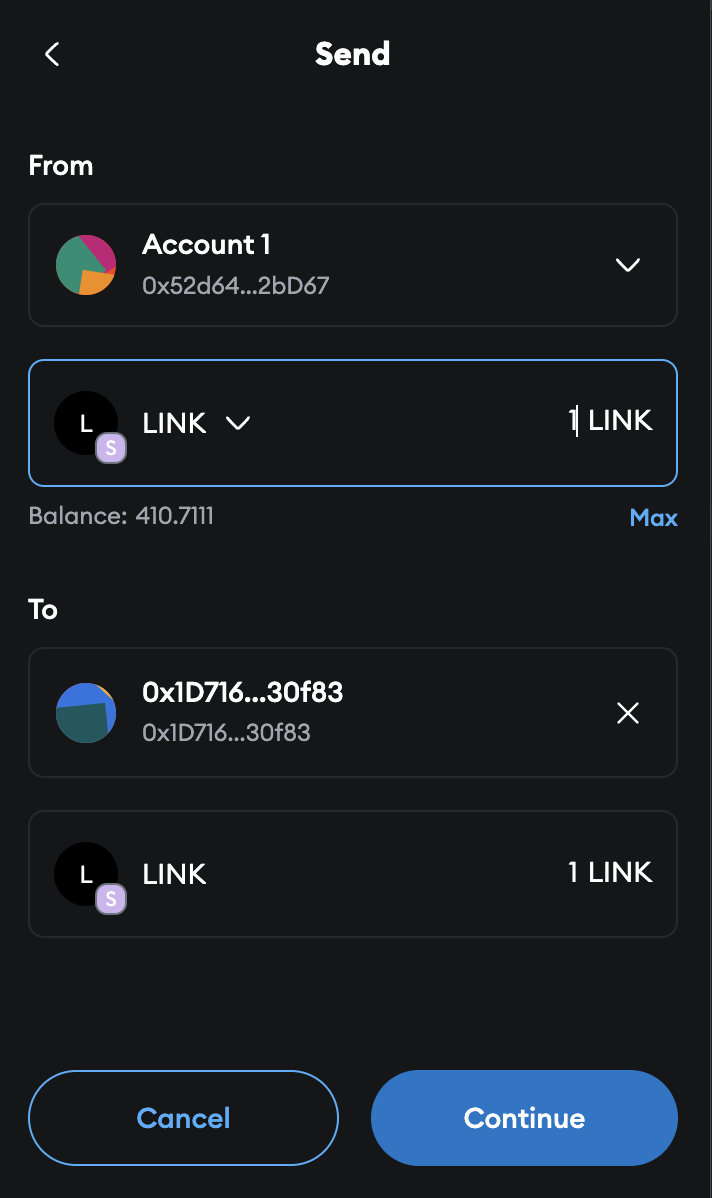 Finally, we need to verify the `StreamsUpkeep` contract. - In Remix, flatten the contract by right-clicking the file and clicking **Flatten** 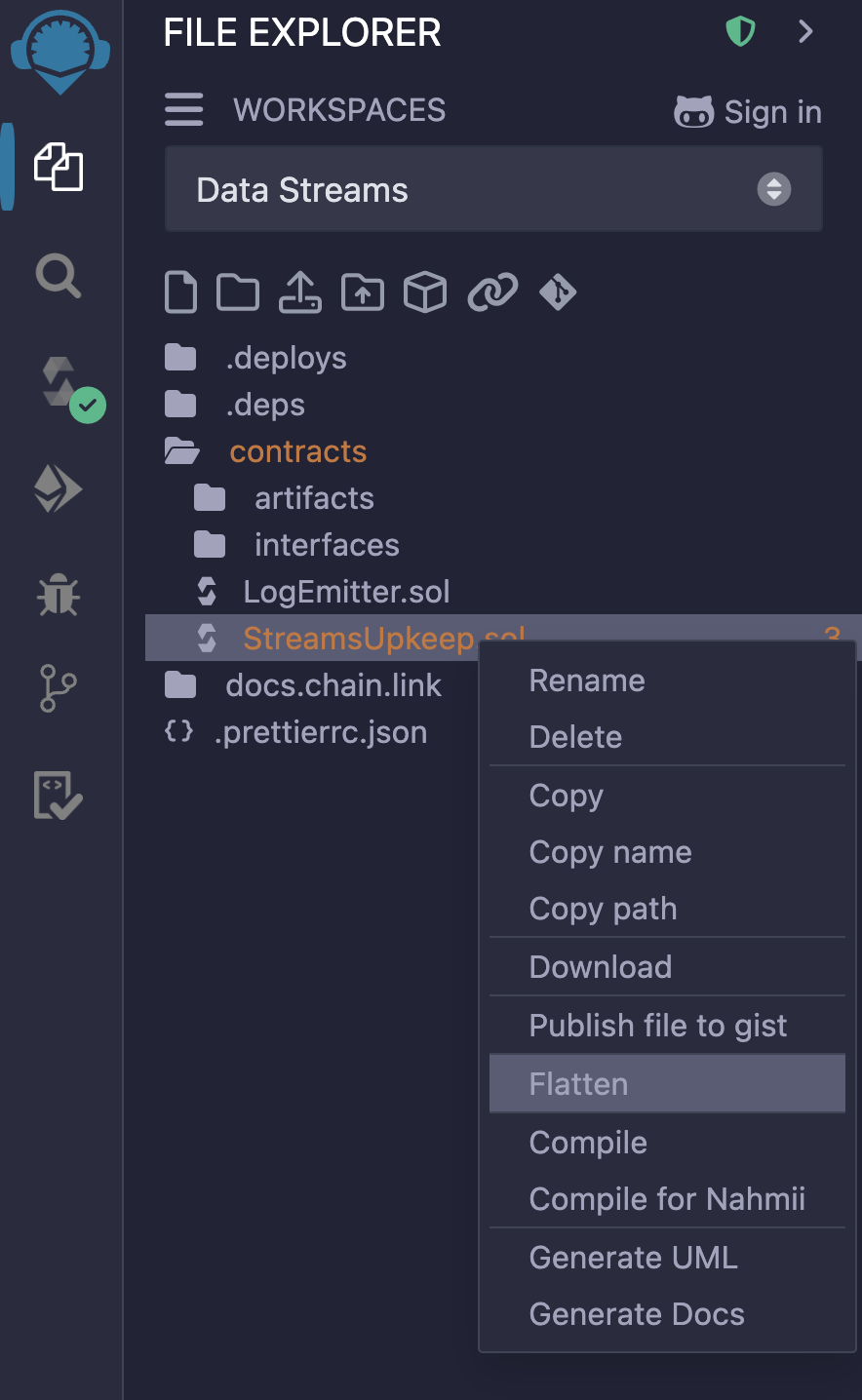 - Head to [Sepolia Etherscan] and search the address of the `StreamsUpkeep` contract. - Click the **Contract** tab and then click **Verify and Publish**. 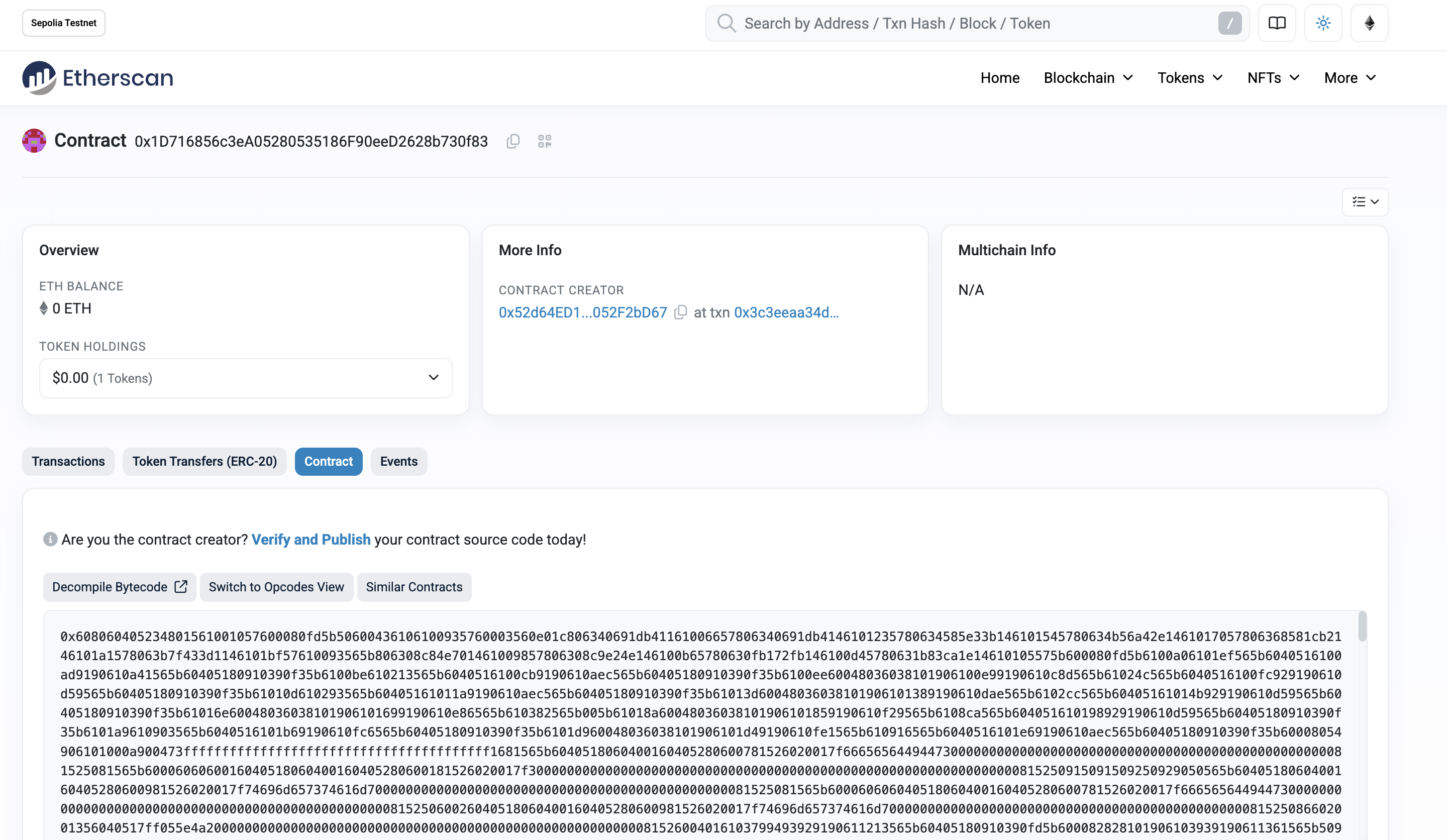 - Select the **Compiler Type** as **Solidity (Single file)** and select the Compiler version and License Type you used. Click **Continue**. 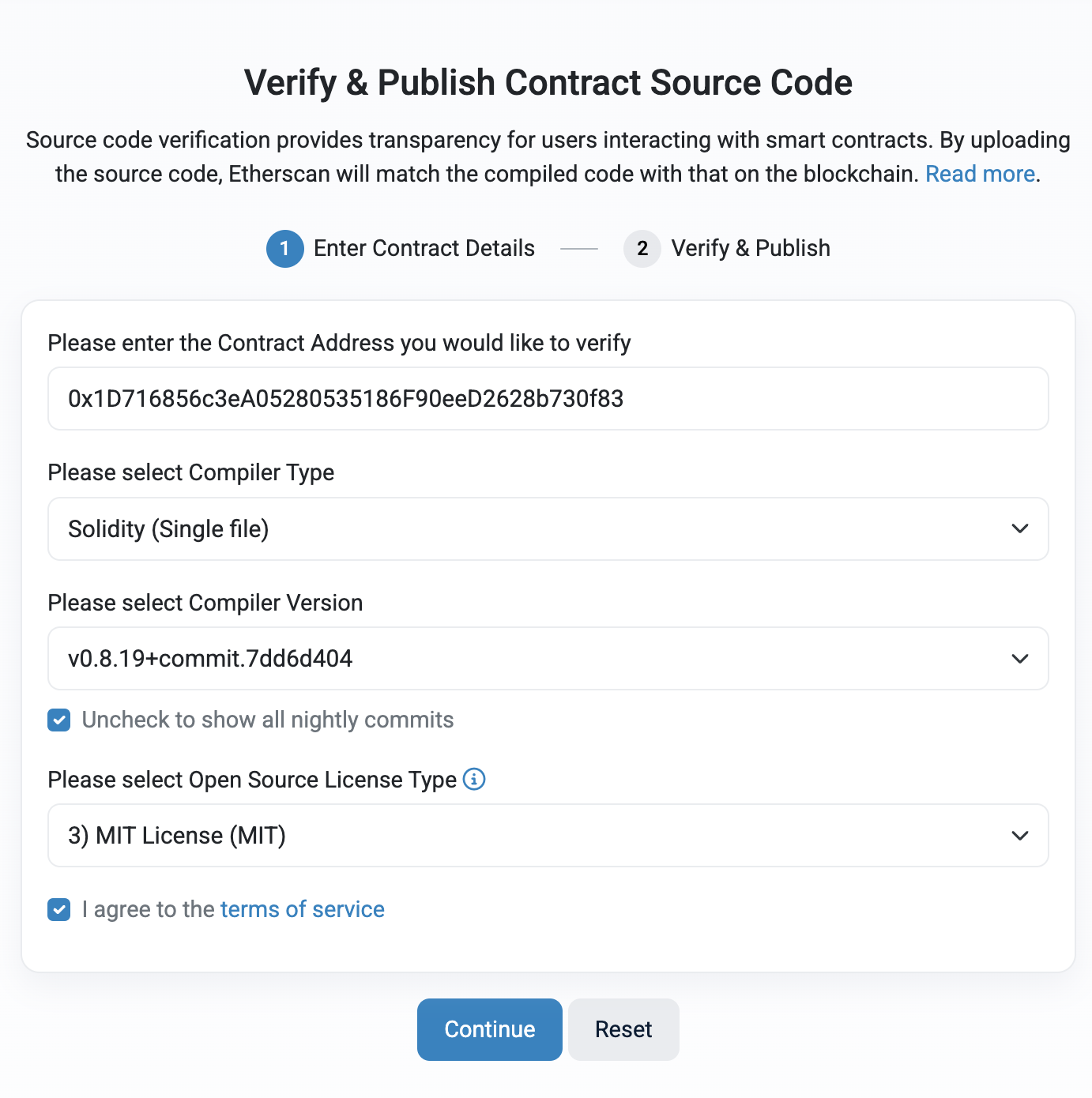 - Go back to Remix and copy the code in the `StreamsUpkeep_flattened.sol` file. Paste this into the source code box. Then click **Verify and Publish**. Note: if it fails, check no constructor arguments were accidentally added. - Your contract will now have a green tick next to the **Contract** tab. ### Register the Upkeep The final step before we actually see this all working in action is to register the `StreamUpkeep` contract for Automation. We need to register a new **Log trigger** upkeep. See [Automation Log Triggers](https://docs.chain.link/chainlink-automation/guides/log-trigger) to learn more about how to register Log Trigger upkeeps. 1. Go to the Automation UI for the chain you are working on. E.g., for [Base Sepolia](https://automation.chain.link/base-sepolia), and connect your wallet. 2. Click **Register new Upkeep**. 3. Select the `Trigger` as **Log trigger** for the upkeep type and click **Next**. 4. Specify the **Contract to automate** as the `StreamsUpkeep` contract address. In this example, you can ignore the warning about the Automation-compatible contract verification. Click **Next**. 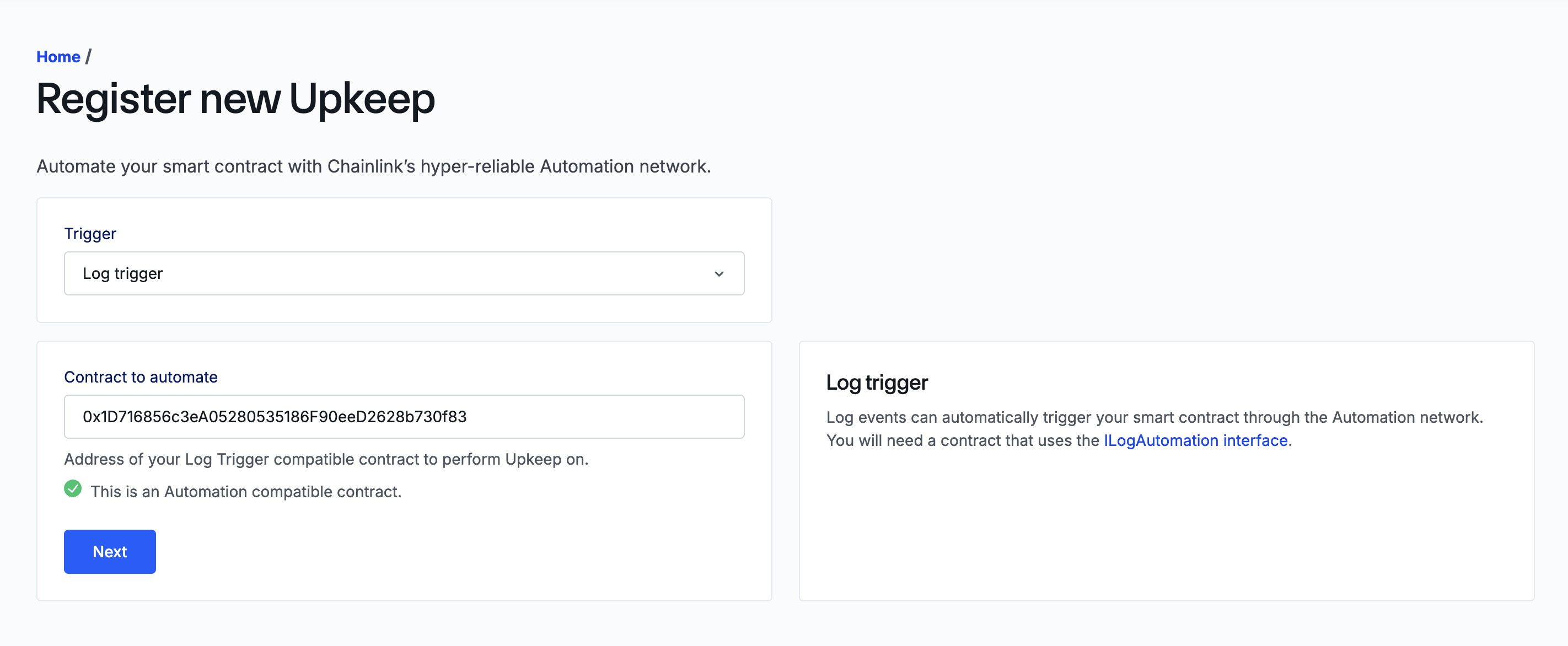 5. Specify the `LogEmitter` contract address to tell Chainlink Automation what contracts to watch for log triggers. Then click **Next**. 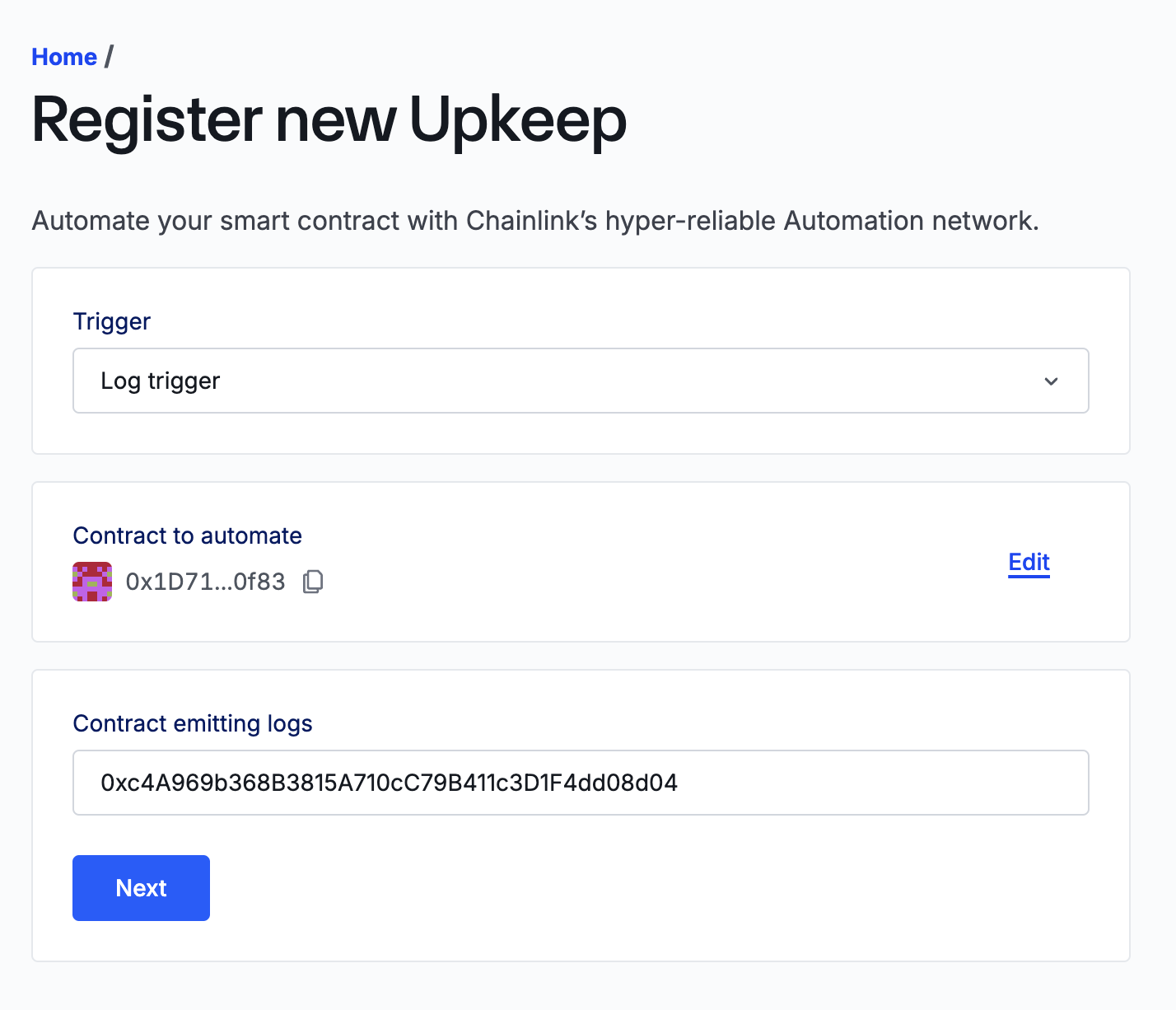 6. Provide the ABI if the contract is not verified. To find the ABI of your contract in Remix, make sure the `LogEmitter` contract is open in the main window and navigate to the **Solidity Compiler** tab. Then, copy the ABI to your clipboard using the button at the bottom of the panel. 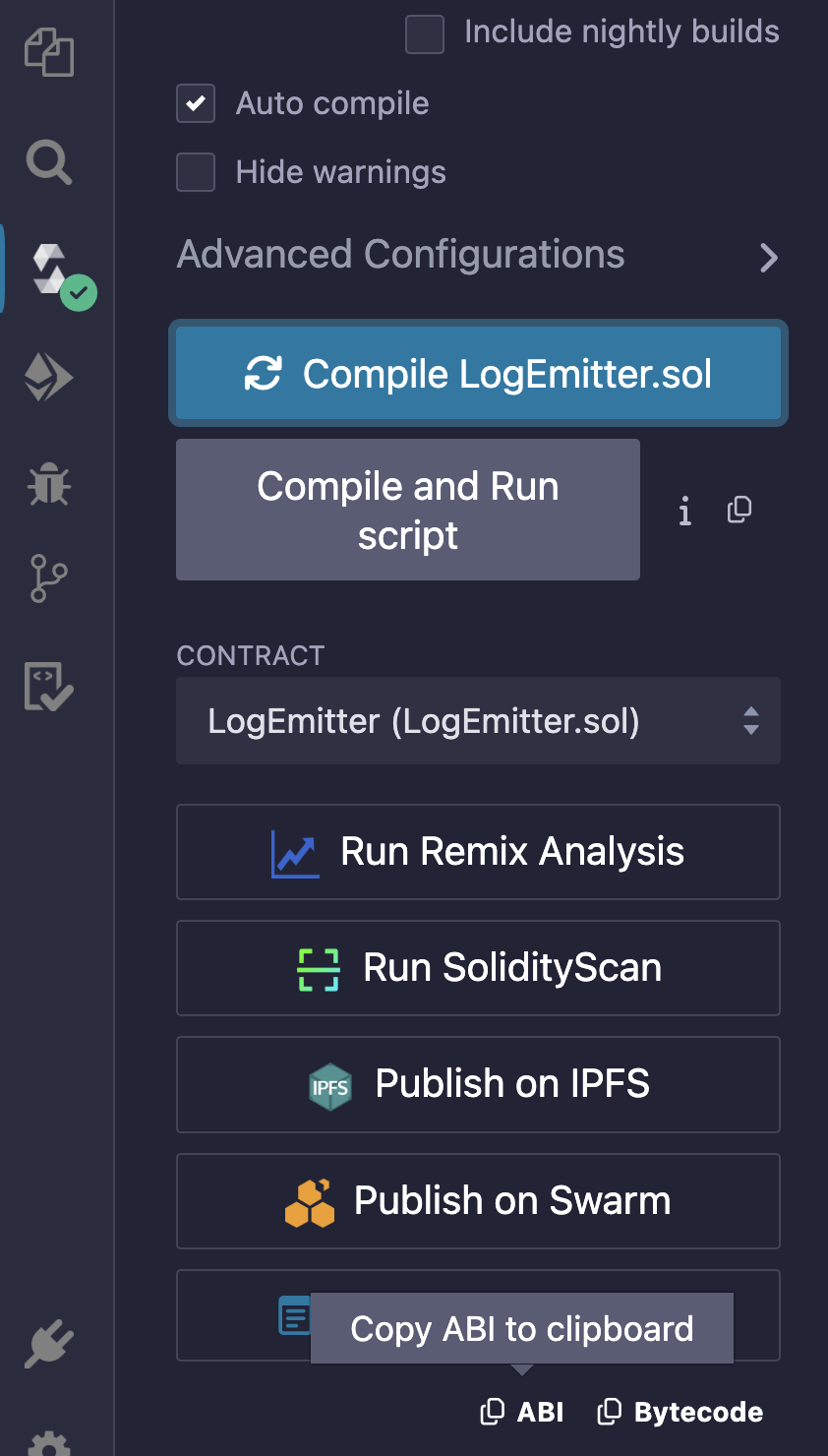 7. Paste the ABI and click **Next**. Leave the **Log index topic filters** box empty and click **Next** again. 8. Give your upkeep a name e.g. "Data Streams Demo" and provide a **Starting balance** of `1` LINK. Leave all other options as they are. Click **Register Upkeep**. 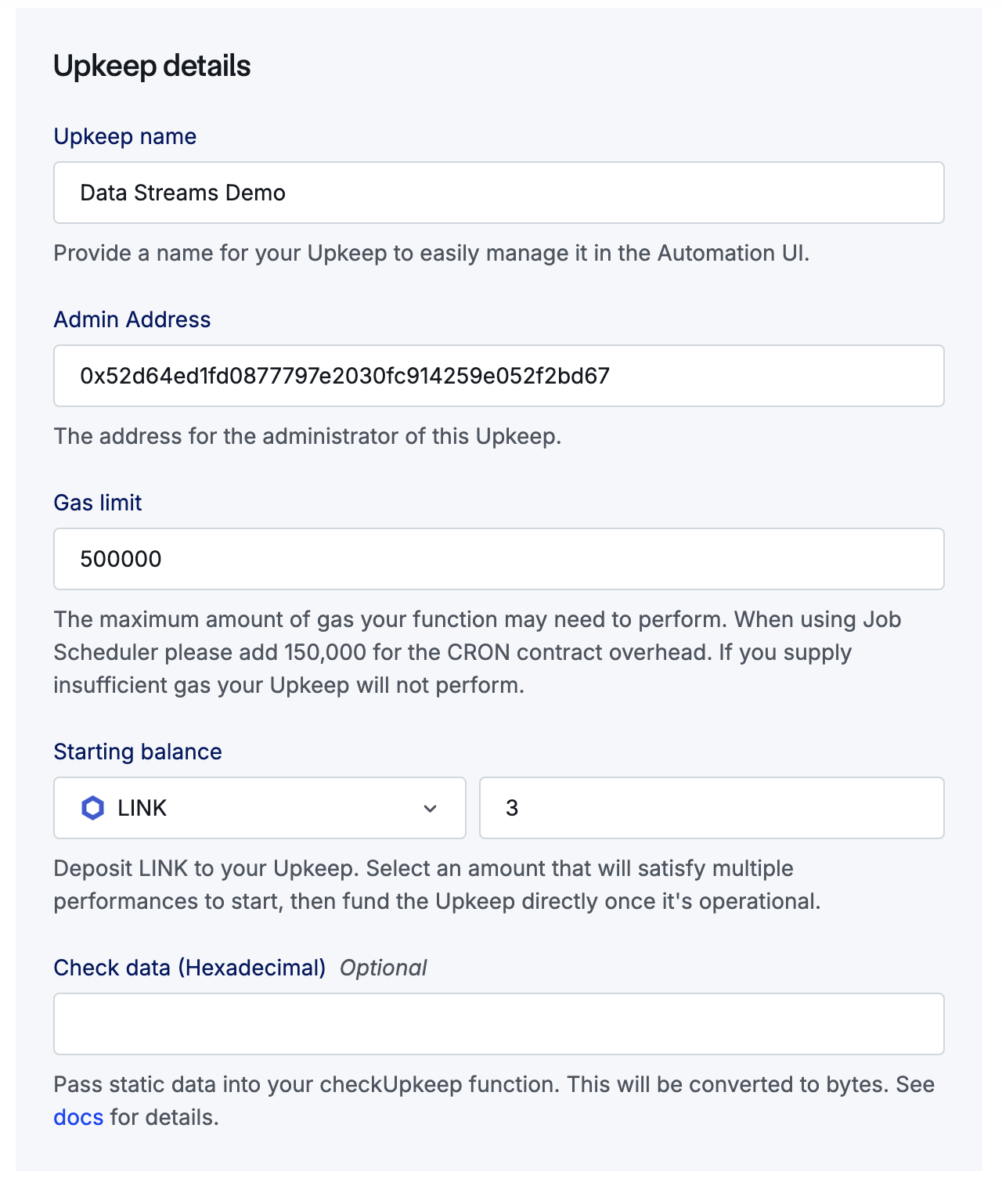 9. Sign the transaction, submit a registration request, and send the LINK to fund the upkeep. 10. Sign the message to verify ownership of the upkeep. 11. Once this has confirmed, click **View Upkeep** to see an overview: 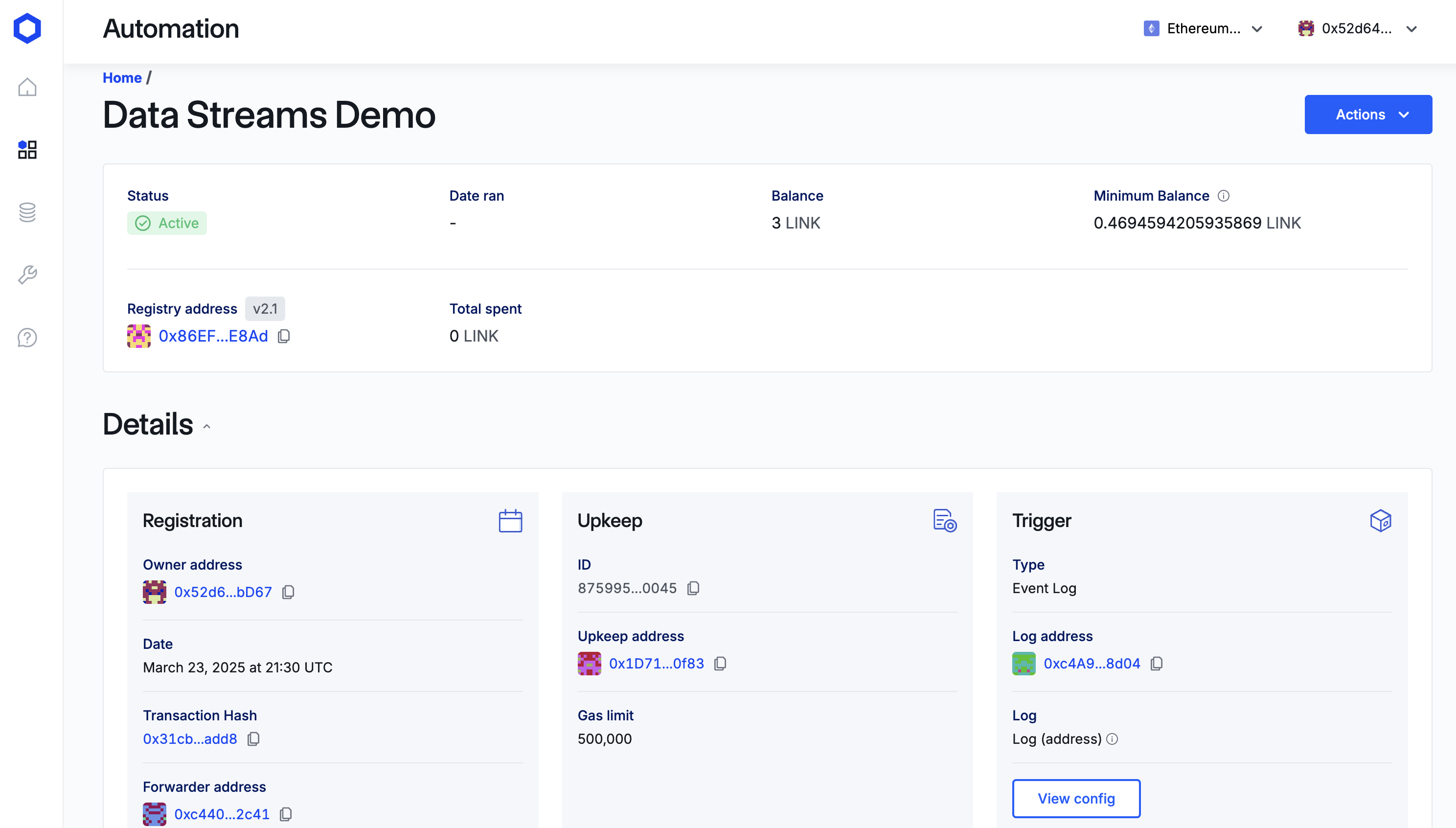 As per Section 4, you will be able to see the upkeep overview, details, and history. ### Fund the StreamsUpkeep contract In this example, the upkeep contract pays for the on-chain verification of reports from Data Streams. The Automation subscription does not cover the cost. Open MetaMask and send 1 testnet LINK on Arbitrum Sepolia to the upkeep contract address you saved earlier. 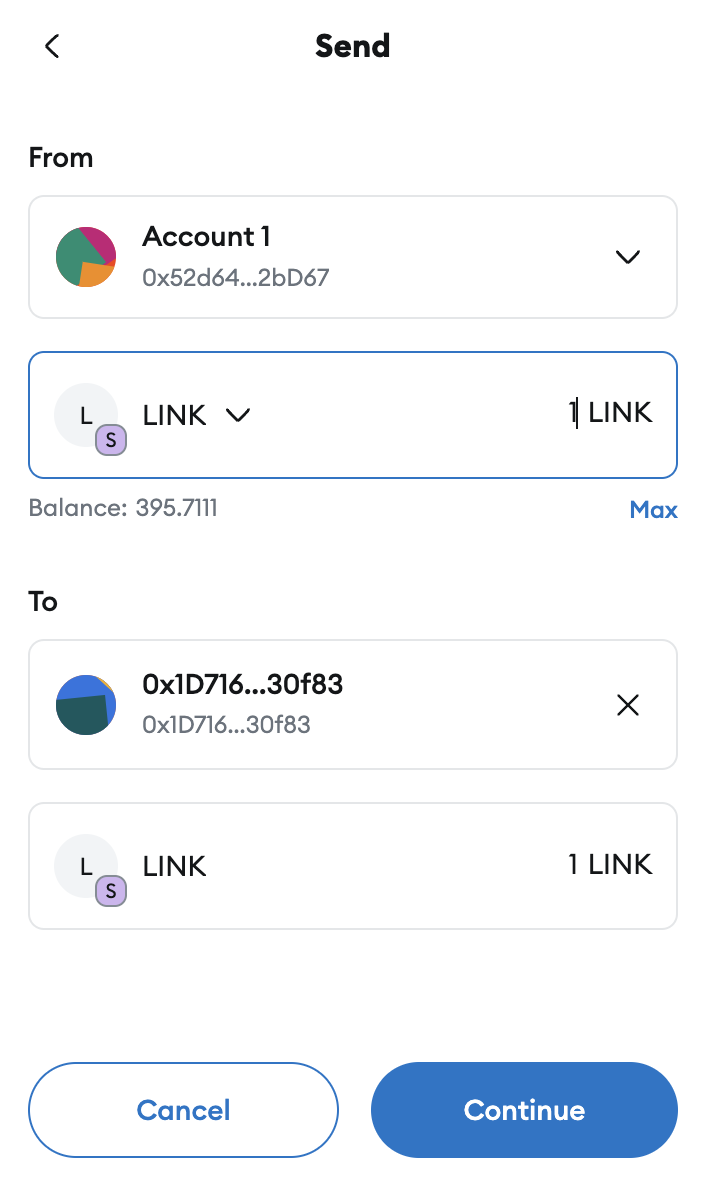 ### Emit a log Finally, let’s call `emitLog` to see this working in action! - Head back to Remix and expand the `LogEmitter` contract in the **Deployed Contracts** section. Click **emitLog** and sign the transaction to call the function and emit the **Log** event. 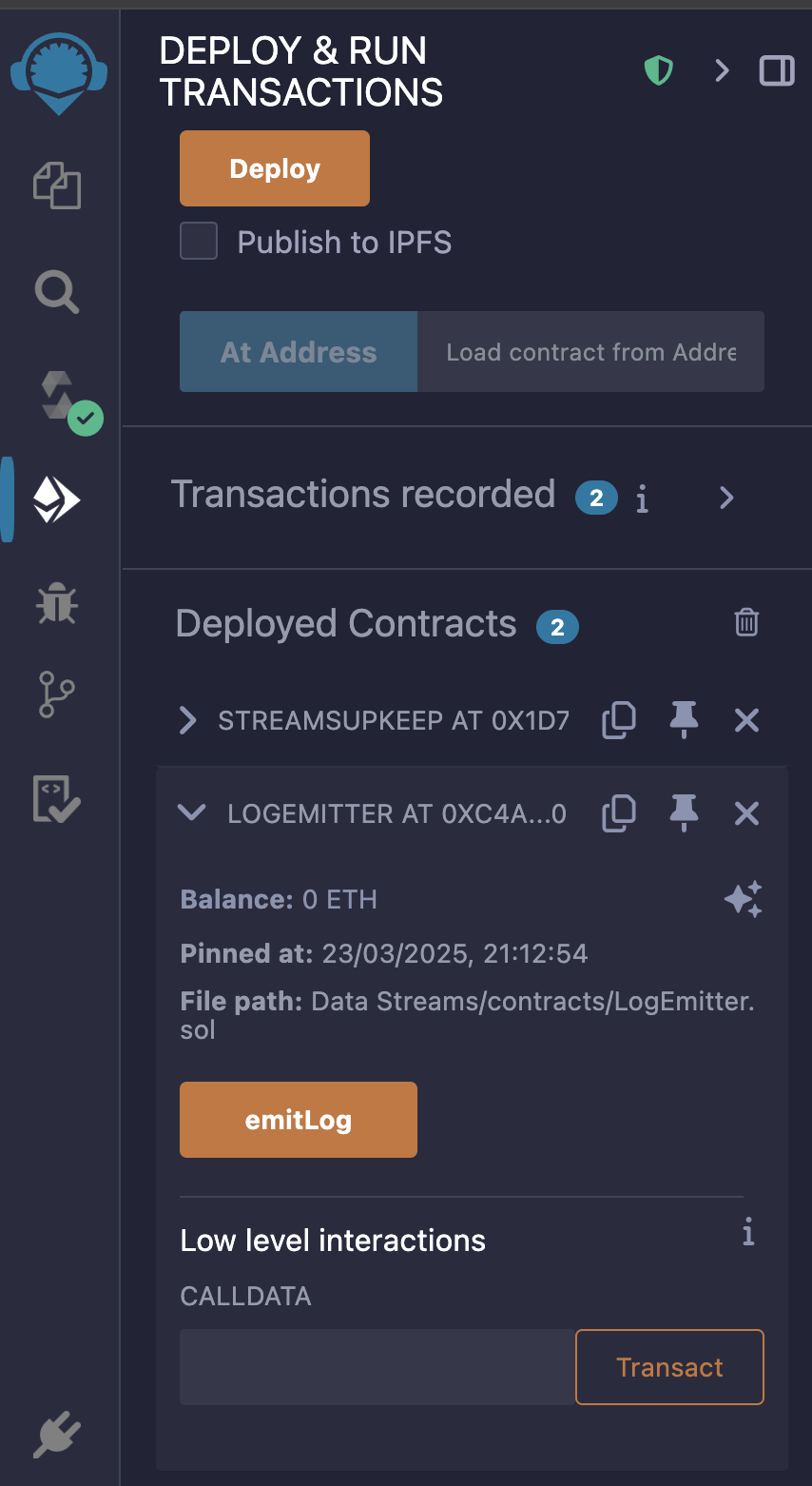 - Sign the transaction and wait for it to confirm. - After the transaction is complete, the log is emitted, and the upkeep is triggered. You can find the upkeep transaction hash in the Chainlink Automation UI. Check to make sure the transaction is successful. 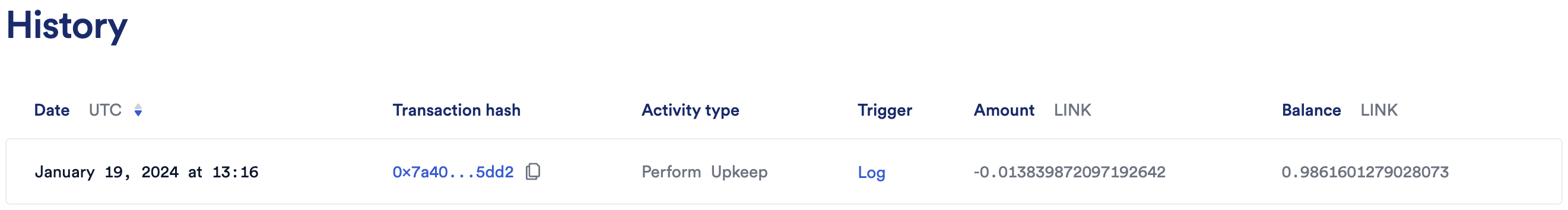 ## View the price The retrieved price is stored in the `lastDecodedPrice` state variable. In the **Deploy & Run Transactions** tab in Remix, expand the details of the `StreamsUpkeep` contract in the **Deployed Contracts** section. Click the `lastDecodedPrice` getter function to view the retrieved price. The answer on the ETH/USD stream uses `18` decimal places, so an answer of `248412100000000000` indicates an ETH/USD price of `2,484.121`. Some streams may use a different number of decimal places for answers. See the [Data Streams Crypto streams page](https://docs.chain.link/data-streams/crypto-streams) for more information. 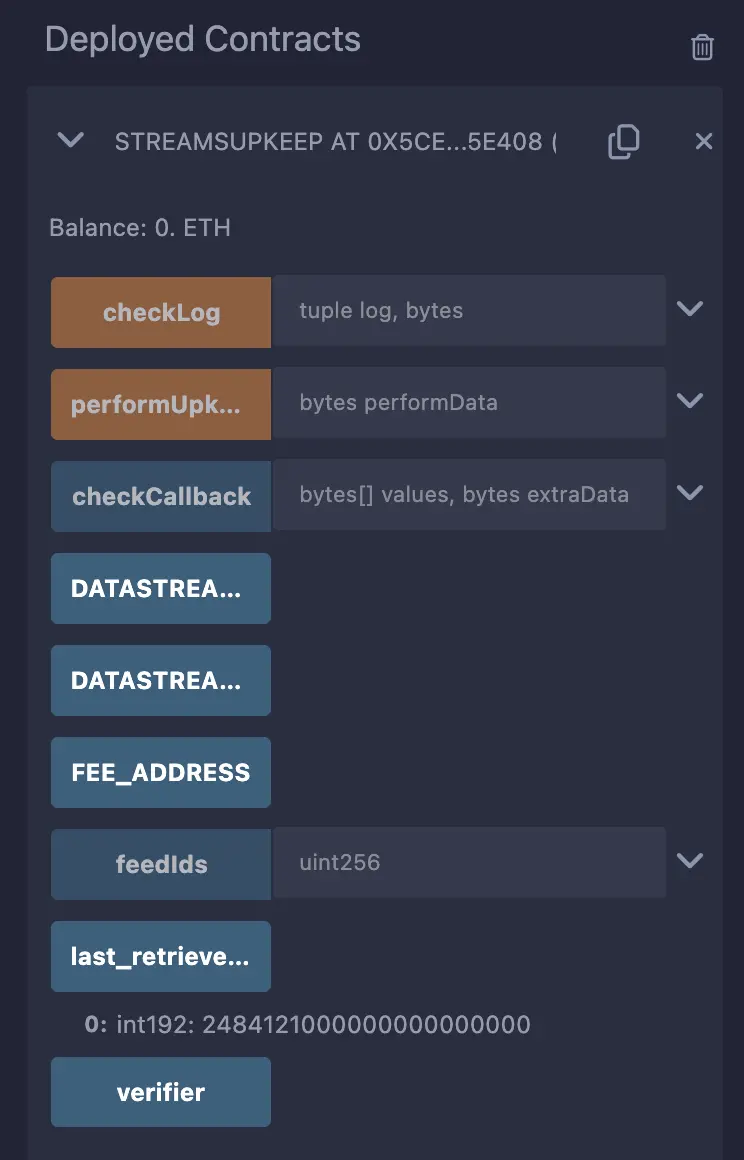 ## (Optional) **EIP-3668: Use of `revert` to convey call information** Clients (e.g., wallets, dApps) must recognize when a function call depends on off-chain data. Instead of modifying ABIs or duplicating functions, EIP-3668 proposes that contracts **revert with specific data** to indicate that off-chain data is needed. The revert message contains information needed for off-chain lookups. This allows: - Clients that understand the EIP-3668 format to fetch the required data and retry the call. - Existing functions to be extended for off-chain lookups without breaking compatibility. ### How It Works 1. A contract function call is made. 2. If the required data is off-chain, the contract **reverts** with structured revert data. 3. A client (e.g., a wallet) intercepts the revert, reads the data, fetches the required off-chain information, and retries the function call with the retrieved data.
Chainlink Data Streams - Streams Trade
This project uses the Streams Trade implementation of Chainlink Data Streams. This implementation uses Chainlink Automation Log Trigger to monitor for an event emission, signaling that data needs to be fetched off-chain.
Please Note:
This section follows a guide in the Chainlink Docs Access Data Streams Using Automation.
This service is restricted to those who gain access to Data Streams from the Chainlink team.
Therefore, it is unlikely that you will be able to reproduce this section of the course, but you can still read our guide and see how Data Streams are used!
How does the Streams Trade implementation work?
An event is emitted from an emitter smart contract, which we will write and name
LogEmitter.We will tell Automation to call a second contract when this event is emitted. When Automation detects the event has been emitted, it runs the
checkLogfunction implemented on the second smart contract which we will write and nameStreamsUpkeep.checkLogand will return a StreamsLookup custom error. Don't worry too much about this right now, we will go through this again as we write the code.Chainlink Automation uses the
StreamsLookupcustom error to retrieve a signed report from the Data Streams Aggregation Network and return the data in a callback to theperformUpkeepfunction.The
performUpkeepfunction verifies the data by calling theverifyfunction on the Chainlink Verifier contract.

Writing the code
We are going to write two smart contracts:
A
LogEmittercontract. This is a simple, smart contract with a single function that emits an event. Automation will pick up this Event to trigger the retrieval of the off-chain data. This function is a simple example in place of an action that a user would perform, such as minting, staking, borrowing, etc.A
StreamsUpkeepcontract. This contract will contain the Automation logic, including:Callback for data processing.
Callback for error processing.
performUpkeepfunction for Automation to return the data.We will request the ETH/USD price stream.
1. LogEmitter contract
First, let’s create a smart contract that emits the event that will trigger Automation to perform an upkeep and retrieve the data from the ETH/USD data stream. Usually, this would be a part of a dApp, and this event would be triggered when a user performs an action such as initiating a trade. We are going to keep this simple.
Create a new workspace called "Data Streams". Make a folder called
contractsand a file calledLogEmitter.solCreate a simple, smart contract with a function called
emitLogthat simply emits an event with the caller address as an indexed parameter.Copy and paste the code from the
LogEmitter.solcontract in the course code repo.
2. StreamsUpkeep contract
Now, let’s write our upkeep smart contract, which Automation will call when LogEmitter::emitLog is called.
Create a file called
StreamsUpkeep.solin thecontractsfolder. In this file, copy and paste the code from theStreamsUpkeep.solcontract in the course code repo.
Note: as of writing, @chainlink v1.3.0 requires you use a compiler version of 0.8.19.
Interfaces
This contract is going to interact with two smart contracts which we need to add interfaces for so that we can call their functions:
1. The FeeManager: allows our smart contract to get the fees for performing the verification
2. The VerifierProxy: this smart contract is responsible for performing the verification of the streams data and also stores the address of the FeeManager contract
-
Add a folder called
interfacesinside yourcontractsfolder, add a file calledIFeeManager.sol, and add the following interface from the course code repo. This is the interface theFeeManagerwill need to conform to which allows callers to get the data streams fees. -
Then, create a file called
IVerifierProxy.sol, again inside that interfaces folder, and add the following interface from the course code repo. This is the interface theVerifierProxycontract will conform to. It allows callers to verify the returned signed data.
Code walkthrough
Let’s now walk through the StreamsUpkeep code so we know what’s happening. As always, this section is optional and targeted toward those who want to understand how to implement Data Streams. Feel free to skip to the deployment section.
Imports
Imports several Chainlink-specific interfaces:
Common: Utilities for working with Chainlink Low Latency Oracle (LLO) feedsStreamsLookupCompatibleInterface: Interface for contracts that work with Streams LookupILogAutomation: Interface for log-triggered automationIRewardManager: Interface for managing rewards in the Chainlink ecosystemIERC20: Standard ERC20 interface for token interactionsThe custom interfaces we just created
Contract declaration
Inherits from two interfaces to be enabled for Chainlink Automation and Data Streams.
Error definition
Defines a custom error for handling unsupported report versions
V3 and V4 Reports
Chainlink Data Streams organize reports in two different standardized formats: the V3 format (used for cryptocurrency assets) and the V4 format (used for real-world assets). Each report format defines a specific set of data fields that contain the price information and related details, as shown in these Solidity structs:
Quote struct
A simple structure to hold token addresses for fee quotes
State variables
There are a few constant variables we need:
DATASTREAMS_FEEDLABEL: This is the first parameter passed to theStreamsLookupcustom error revert. We will explain the custom error shortly, butDATASTREAMS_FEEDLABELis a string that specifies the feed IDs that will be provided. The only allowed value is"feedIDs"DATASTREAMS_QUERYLABEL: This is the third parameter passed to theStreamsLookupcustom error calledtimeParamKey. The only allowed value is“timestamp”.VERIFIER: the address of the Chainlink verifier(there is one verifier contract deployed on all available chains) on the specific chain you are working on.
Additionally, we need to save the
feedIdsin a string array state variable. This is the ID for the specific stream (e.g., forETH/USDthe ID is"0x000359843a543ee2fe414dc14c7e7920ef10f4372990b79d6361cdc0dd1ba782"on testnet).The full list of verifier addresses and feed IDs can be found in the Chainlink documentation:
checkLog function
The checkLog function is the function called by Automation when it detects the event emission. The code example uses revert with the StreamsLookup custom error to convey all the information about what stream(s) to retrieve. This use of revert is part of the EIP-3668 specification, which proposes that contracts revert with specific data to indicate that off-chain data is needed. The revert message contains information needed for off-chain lookups.
It intentionally reverts with a special error that contains:
ID of the feed to fetch data from.
A timestamp for context.
Chainlink nodes catch this revert and use it to fetch data from Data Streams. More information on EIP-3668 can be found at the end of this lesson.
checkCallback function
The following function is a callback function (which is simulated off-chain, hence why it is pure), so it can be modified to further process the report data. The report and data are then passed into performUpkeep by Automation.
performUpkeep function
performUpkeep is the function that is executed on-chain by Automation. It contains the logic to process the data and record it on-chain. In this function, we are simply:
Decoding the
performDataExtracting the report
Validating the report version
Approving the fees to be paid
Verifying the report
Decoding the report into the relevant struct (V3 or V4)
Storing the report data in a state variable
lastDecodedPrice.
checkErrorHandler function
Finally, the checkErrorHandler function is included to show you how you can implement logic into this function to surface any errors. In this example, we have kept things simple and hardcoded it to return true for upkeepNeeded (aka, always fetch a report) and not pass any performData:
Compile and deploy the contracts
Compile and deploy both the StreamsUpkeep and LogEmitter contracts to Sepolia using the steps detailed in Section 2. Make sure you pin both contracts to your workspace.
Fund the StreamsUpkeep with LINK
To pay for Automation, we need to fund our StreamsUpkeep contract with LINK.
In Metamask, click the LINK token in the Tokens tab, then click the Send button.
Send 1 LINK to the StreamsUpkeep address (that you just deployed).
- Enter the contract address of the StreamUpkeep contract as the To address (you can copy the address in Remix)
- Enter the amount as 1.
Click Continue and then sign the transaction by clicking Confirm to fund the contract with LINK.

Finally, we need to verify the StreamsUpkeep contract.
In Remix, flatten the contract by right-clicking the file and clicking Flatten

Head to [Sepolia Etherscan] and search the address of the
StreamsUpkeepcontract.Click the Contract tab and then click Verify and Publish.

Select the Compiler Type as Solidity (Single file) and select the Compiler version and License Type you used. Click Continue.

Go back to Remix and copy the code in the
StreamsUpkeep_flattened.solfile. Paste this into the source code box. Then click Verify and Publish. Note: if it fails, check no constructor arguments were accidentally added.Your contract will now have a green tick next to the Contract tab.
Register the Upkeep
The final step before we actually see this all working in action is to register the StreamUpkeep contract for Automation. We need to register a new Log trigger upkeep. See Automation Log Triggers to learn more about how to register Log Trigger upkeeps.
Go to the Automation UI for the chain you are working on. E.g., for Base Sepolia, and connect your wallet.
Click Register new Upkeep.
Select the
Triggeras Log trigger for the upkeep type and click Next.Specify the Contract to automate as the
StreamsUpkeepcontract address. In this example, you can ignore the warning about the Automation-compatible contract verification. Click Next.

Specify the
LogEmittercontract address to tell Chainlink Automation what contracts to watch for log triggers. Then click Next.

Provide the ABI if the contract is not verified. To find the ABI of your contract in Remix, make sure the
LogEmittercontract is open in the main window and navigate to the Solidity Compiler tab. Then, copy the ABI to your clipboard using the button at the bottom of the panel.

-
Paste the ABI and click Next. Leave the Log index topic filters box empty and click Next again.
-
Give your upkeep a name e.g. "Data Streams Demo" and provide a Starting balance of
1LINK. Leave all other options as they are. Click Register Upkeep.

Sign the transaction, submit a registration request, and send the LINK to fund the upkeep.
Sign the message to verify ownership of the upkeep.
Once this has confirmed, click View Upkeep to see an overview:

As per Section 4, you will be able to see the upkeep overview, details, and history.
Fund the StreamsUpkeep contract
In this example, the upkeep contract pays for the on-chain verification of reports from Data Streams. The Automation subscription does not cover the cost.
Open MetaMask and send 1 testnet LINK on Arbitrum Sepolia to the upkeep contract address you saved earlier.

Emit a log
Finally, let’s call emitLog to see this working in action!
Head back to Remix and expand the
LogEmittercontract in the Deployed Contracts section. Click emitLog and sign the transaction to call the function and emit the Log event.

-
Sign the transaction and wait for it to confirm.
-
After the transaction is complete, the log is emitted, and the upkeep is triggered. You can find the upkeep transaction hash in the Chainlink Automation UI. Check to make sure the transaction is successful.

View the price
The retrieved price is stored in the lastDecodedPrice state variable.
In the Deploy & Run Transactions tab in Remix, expand the details of the StreamsUpkeep contract in the Deployed Contracts section.
Click the lastDecodedPrice getter function to view the retrieved price. The answer on the ETH/USD stream uses 18 decimal places, so an answer of 248412100000000000 indicates an ETH/USD price of 2,484.121. Some streams may use a different number of decimal places for answers. See the Data Streams Crypto streams page for more information.

(Optional) EIP-3668: Use of revert to convey call information
Clients (e.g., wallets, dApps) must recognize when a function call depends on off-chain data.
Instead of modifying ABIs or duplicating functions, EIP-3668 proposes that contracts revert with specific data to indicate that off-chain data is needed. The revert message contains information needed for off-chain lookups. This allows:
Clients that understand the EIP-3668 format to fetch the required data and retry the call.
Existing functions to be extended for off-chain lookups without breaking compatibility.
How It Works
A contract function call is made.
If the required data is off-chain, the contract reverts with structured revert data.
A client (e.g., a wallet) intercepts the revert, reads the data, fetches the required off-chain information, and retries the function call with the retrieved data.
Data Streams In A Smart Contract
A hands-on walkthrough to Chainlink Data Streams - Streams Trade - Learn to implement the event-driven Streams Trade pattern using Automation Log Triggers. Code, deploy, and register the necessary contracts (`LogEmitter`, `StreamsUpkeep`) to fetch and verify Data Streams reports.
Previous lesson
Previous
Next lesson
Next
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Smart contract and Solidity fundamentals
Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network (DON)
Chainlink Data Feeds
Chainlink Data Streams
Chainlink Automation
Chainlink CCIP
Chainlink Functions
Verifiable Random Function (VRF)
Chainlink Proof of Reserve
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Smart Contract Developers
- Solutions Architects
- Blockchain Engineers
- Web3 Developers
- Security Researchers
Potential Careers
Smart Contract Engineer
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
DeFi Developer
$75,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 developer
$60,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 Developer Relations
$85,000 - $125,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Blockchain Financial Analyst
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Last updated on July 25, 2025
Duration: 9min
Duration: 1h 17min
Duration: 42min
Duration: 30min
Duration: 1h 03min
Duration: 49min
Duration: 30min
Duration: 19min
Duration: 37min
Duration: 30min
Certification: Chainlink Fundamentals
The Chainlink Fundamentals proficiency exam covers is designed to confirm your grasp of all key concepts and learnings presented in the course material. Exam takers will have 75 minutes to complete 50 questions and must score 30/50 to pass and earn a Certificate of Completion. Because course material is continually updated, The Chainlink Fundamentals Certificate of Completions expires after 1 year. To remain current, holders must re-take the exam and pass to confirm their current knowledge.
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Smart contract and Solidity fundamentals
Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network (DON)
Chainlink Data Feeds
Chainlink Data Streams
Chainlink Automation
Chainlink CCIP
Chainlink Functions
Verifiable Random Function (VRF)
Chainlink Proof of Reserve
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Smart Contract Developers
- Solutions Architects
- Blockchain Engineers
- Web3 Developers
- Security Researchers
Potential Careers
Smart Contract Engineer
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
DeFi Developer
$75,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 developer
$60,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 Developer Relations
$85,000 - $125,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Blockchain Financial Analyst
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Last updated on July 25, 2025

