# Chainlink Data Streams Chainlink Data Streams has the following core components: 1. **A Chainlink Decentralized Oracle Network (DON)**: For Data Streams, the Chainlink DON operates similarly to the DONs that power Chainlink Data Feeds, but rather than directly delivering the data onchain, DONs sign and deliver reports to the Chainlink Data Streams Aggregation Network. This enables the Data Streams DON to deliver reports more frequently (often with with sub-second latency) for time-sensitive applications. Nodes in the DON retrieve data from many different data providers, reach a consensus about the median price of an asset, sign a report including that data, and deliver the report to the Data Streams Aggregation Network. 2. **The Chainlink Data Streams Aggregation Network**: The Data Streams Aggregation Network stores the signed reports and makes them available for retrieval. The network is highly available and resilient because it uses what’s known as an “active-active multi-site deployment” architecture. This means that infrastructure is distributed across multiple geographical sites. In this setup, all sites are active simultaneously, meaning they can independently handle requests and respond to users. This simultaneous and parallel operation ensures high availability and robust fault tolerance. These reports can then be “pulled” by consumers of Data Streams in one of two ways: 1. Chainlink Automation may request reports on behalf of a dApp (known as Streams Trade) or 2. Reports may be requested directly via the API (known as Streams Direct). 3. **The Chainlink Verifier Contract**: This smart contract verifies the signature from the DON, cryptographically guaranteeing that the report has not been altered from the time that the DON signed the data and the point where a dApp pulls the data into the application. ## Available Chainlink Data Streams Chainlink Data Streams primarily provide market pricing data for assets. Pricing data is always delivered relative to another asset, so the data is presented as “pairs”; for example ETH/USD is the price of ETH as denominated in USD. Data Streams for specific pairs are available on certain blockchains. You can look up the pairs and chains where Data Streams are supported through https://data.chain.link/. When presented with the below screen, click on “Data Streams”.  That will take you to https://data.chain.link/streams—which looks like this: 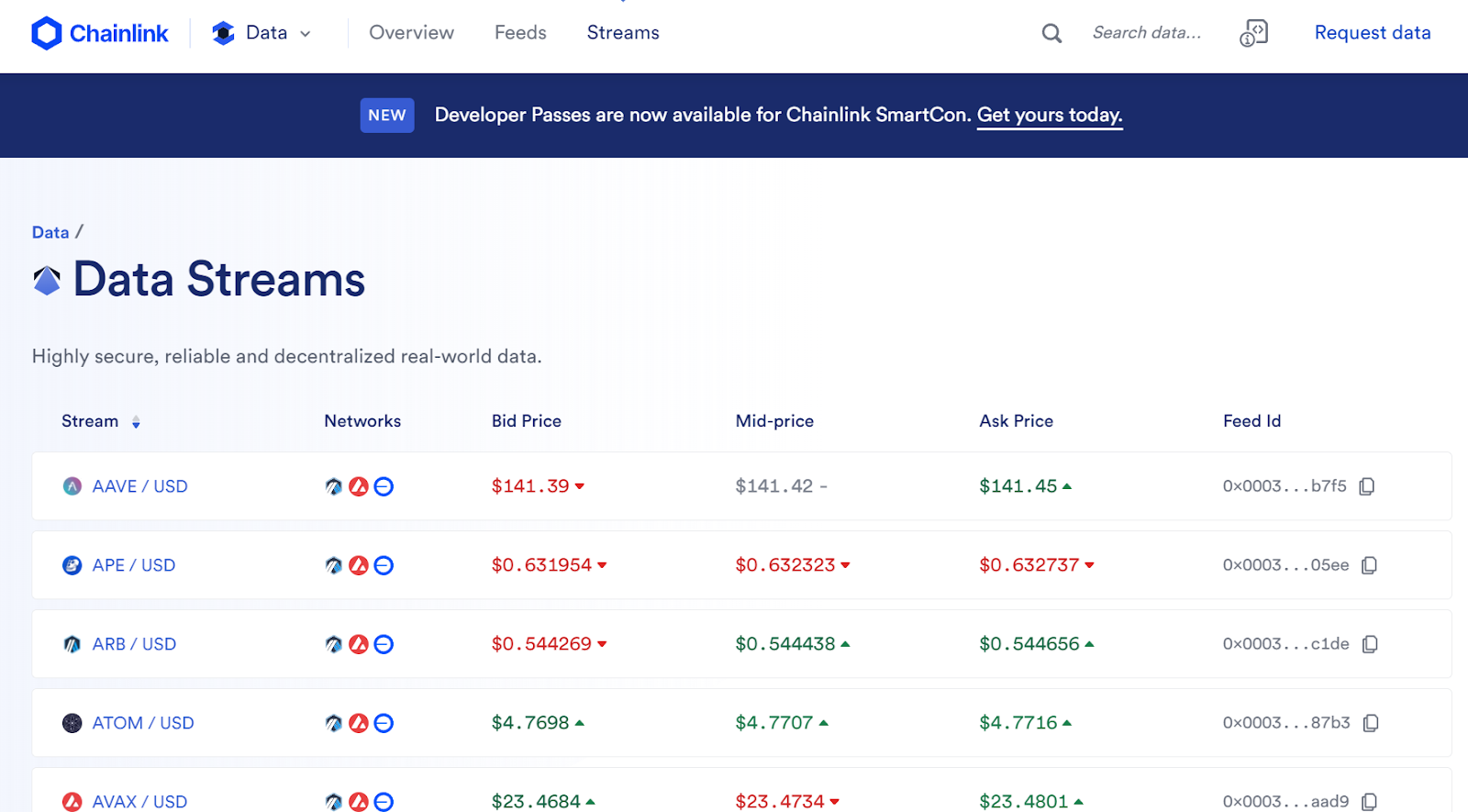 If you click on any of the Pairs in the “Stream” Column, it will take you to the page which has important configuration details such as that asset pair’s “feed id”, bid and ask prices, and more. ## Chainlink Data Streams Use cases Pull-based oracles enable decentralized applications to access cryptographically verifiable data that is updated at a high frequency and delivered with low latency. These properties unlock several new use cases: 1. **Perpetual Futures**: A type of financial contract that lets you lock in on an expected future price of an asset. By providing low-latency price data and helping mitigate against frontrunning, Chainlink Data Streams enables perpetual futures protocols deployed to blockchains to compete with traditional centralized exchanges on performance and reliability without sacrificing the inherent transparency of onchain applications. 2. **Options**: An options contract gives a user the right to buy or sell an asset at a preset price before a certain date to protect against anticipated price gains or falls. For options protocols, Chainlink Data Streams enable timely and precise settlement (i.e. execution and fulfillment) of onchain options contracts. Additionally, Data Streams provides more detailed asset liquidity data, unlocking dynamic onchain risk management logic in the protocol to assist market participants. 3. **Prediction Markets**: Prediction markets enable participants to protect against loss or capture gains from future outcomes. Higher frequency data updates unlock faster markets so that users are able to act quickly in response to real-time events and be confident in the accuracy of the data used in the settlement of those contracts. Ultimately, Chainlink Data Streams makes financial tools work better by delivering fast and accurate data without compromising on security or transparency—a critical innovation for a trustless ecosystem. You can learn how to use Chainlink Data Streams in your dApp by visiting the documentation here: https://docs.chain.link/data-streams
Chainlink Data Streams
Chainlink Data Streams has the following core components:
-
A Chainlink Decentralized Oracle Network (DON): For Data Streams, the Chainlink DON operates similarly to the DONs that power Chainlink Data Feeds, but rather than directly delivering the data onchain, DONs sign and deliver reports to the Chainlink Data Streams Aggregation Network. This enables the Data Streams DON to deliver reports more frequently (often with with sub-second latency) for time-sensitive applications. Nodes in the DON retrieve data from many different data providers, reach a consensus about the median price of an asset, sign a report including that data, and deliver the report to the Data Streams Aggregation Network.
-
The Chainlink Data Streams Aggregation Network: The Data Streams Aggregation Network stores the signed reports and makes them available for retrieval. The network is highly available and resilient because it uses what’s known as an “active-active multi-site deployment” architecture. This means that infrastructure is distributed across multiple geographical sites. In this setup, all sites are active simultaneously, meaning they can independently handle requests and respond to users. This simultaneous and parallel operation ensures high availability and robust fault tolerance. These reports can then be “pulled” by consumers of Data Streams in one of two ways:
Chainlink Automation may request reports on behalf of a dApp (known as Streams Trade) or
Reports may be requested directly via the API (known as Streams Direct).
-
The Chainlink Verifier Contract: This smart contract verifies the signature from the DON, cryptographically guaranteeing that the report has not been altered from the time that the DON signed the data and the point where a dApp pulls the data into the application.
Available Chainlink Data Streams
Chainlink Data Streams primarily provide market pricing data for assets. Pricing data is always delivered relative to another asset, so the data is presented as “pairs”; for example ETH/USD is the price of ETH as denominated in USD.
Data Streams for specific pairs are available on certain blockchains. You can look up the pairs and chains where Data Streams are supported through https://data.chain.link/.
When presented with the below screen, click on “Data Streams”.

That will take you to https://data.chain.link/streams—which looks like this:

If you click on any of the Pairs in the “Stream” Column, it will take you to the page which has important configuration details such as that asset pair’s “feed id”, bid and ask prices, and more.
Chainlink Data Streams Use cases
Pull-based oracles enable decentralized applications to access cryptographically verifiable data that is updated at a high frequency and delivered with low latency. These properties unlock several new use cases:
-
Perpetual Futures: A type of financial contract that lets you lock in on an expected future price of an asset. By providing low-latency price data and helping mitigate against frontrunning, Chainlink Data Streams enables perpetual futures protocols deployed to blockchains to compete with traditional centralized exchanges on performance and reliability without sacrificing the inherent transparency of onchain applications.
-
Options: An options contract gives a user the right to buy or sell an asset at a preset price before a certain date to protect against anticipated price gains or falls. For options protocols, Chainlink Data Streams enable timely and precise settlement (i.e. execution and fulfillment) of onchain options contracts. Additionally, Data Streams provides more detailed asset liquidity data, unlocking dynamic onchain risk management logic in the protocol to assist market participants.
-
Prediction Markets: Prediction markets enable participants to protect against loss or capture gains from future outcomes. Higher frequency data updates unlock faster markets so that users are able to act quickly in response to real-time events and be confident in the accuracy of the data used in the settlement of those contracts.
Ultimately, Chainlink Data Streams makes financial tools work better by delivering fast and accurate data without compromising on security or transparency—a critical innovation for a trustless ecosystem.
You can learn how to use Chainlink Data Streams in your dApp by visiting the documentation here: https://docs.chain.link/data-streams
Introduction To Data Streams
A detailed exploration of Chainlink Data Streams - Delve into the core components like the DON, Aggregation Network, and Verifier Contract, and how pull-based oracles deliver low-latency data. Understand its key use cases in DeFi, including perpetual futures, options, and prediction markets.
Previous lesson
Previous
Next lesson
Next
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Smart contract and Solidity fundamentals
Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network (DON)
Chainlink Data Feeds
Chainlink Data Streams
Chainlink Automation
Chainlink CCIP
Chainlink Functions
Verifiable Random Function (VRF)
Chainlink Proof of Reserve
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Smart Contract Developers
- Solutions Architects
- Blockchain Engineers
- Web3 Developers
- Security Researchers
Potential Careers
Smart Contract Engineer
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
DeFi Developer
$75,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 developer
$60,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 Developer Relations
$85,000 - $125,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Blockchain Financial Analyst
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Last updated on July 25, 2025
Duration: 9min
Duration: 1h 17min
Duration: 42min
Duration: 30min
Duration: 1h 03min
Duration: 49min
Duration: 30min
Duration: 19min
Duration: 37min
Duration: 30min
Certification: Chainlink Fundamentals
The Chainlink Fundamentals proficiency exam covers is designed to confirm your grasp of all key concepts and learnings presented in the course material. Exam takers will have 75 minutes to complete 50 questions and must score 30/50 to pass and earn a Certificate of Completion. Because course material is continually updated, The Chainlink Fundamentals Certificate of Completions expires after 1 year. To remain current, holders must re-take the exam and pass to confirm their current knowledge.
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Smart contract and Solidity fundamentals
Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network (DON)
Chainlink Data Feeds
Chainlink Data Streams
Chainlink Automation
Chainlink CCIP
Chainlink Functions
Verifiable Random Function (VRF)
Chainlink Proof of Reserve
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Smart Contract Developers
- Solutions Architects
- Blockchain Engineers
- Web3 Developers
- Security Researchers
Potential Careers
Smart Contract Engineer
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
DeFi Developer
$75,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 developer
$60,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Web3 Developer Relations
$85,000 - $125,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Blockchain Financial Analyst
$100,000 - $150,000 (avg. salary)
Last updated on July 25, 2025

