_Follow along with this video:_ --- ### Starting with the Code What I like to do when first assessing a codebase is to start at the `main entry point`. Sometimes this area of a protocol may be a little unclear, but using Solidity: Metrics can help us out a lot. 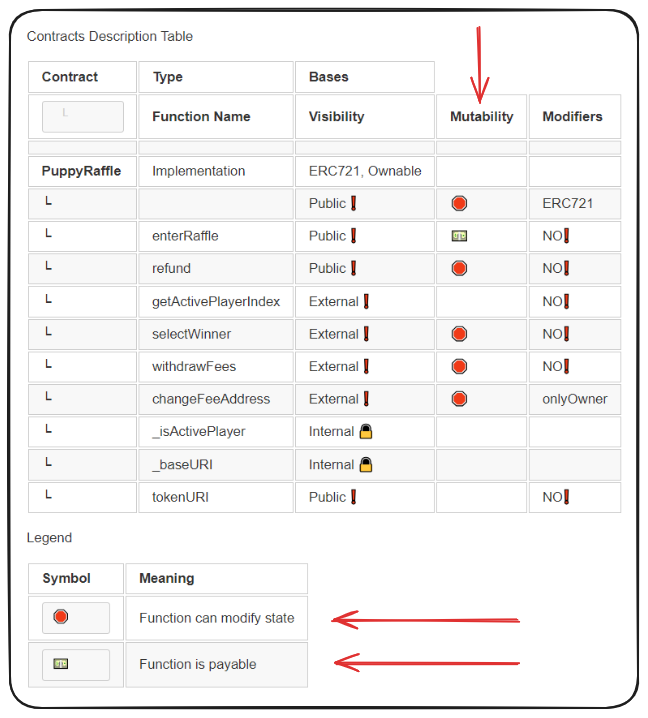 Pay special attention to the functions marked `public` or `external`. Especially those which `modify state` or are `payable`. These are going to be certain potential attack vectors. > **Note:** In Foundry you can use the command `forge inspect PuppyRaffle methods` to receive an output of methods for the contract. I would start with the `enterRaffle` function. Let's take a look. ```js /// @notice this is how players enter the raffle /// @notice they have to pay the entrance fee * the number of players /// @notice duplicate entrants are not allowed /// @param newPlayers the list of players to enter the raffle function enterRaffle(address[] memory newPlayers) public payable { require(msg.value == entranceFee * newPlayers.length, "PuppyRaffle: Must send enough to enter raffle"); for (uint256 i = 0; i < newPlayers.length; i++) { players.push(newPlayers[i]); } // Check for duplicates for (uint256 i = 0; i < players.length - 1; i++) { for (uint256 j = i + 1; j < players.length; j++) { require(players[i] != players[j], "PuppyRaffle: Duplicate player"); } } emit RaffleEnter(newPlayers); } ``` Starting with the `NatSpec` we may have a few questions rise. - _What's meant by # of players?_ - _How does the function prevent duplicate entrants?_ Write questions like these in your `notes.md` or even as `@audit` notes inline. These are things we'll want to answer as we progress through the code. ### One thing I notice in our next few lines is - I don't really love their naming conventions. `entranceFee` is immutable and nothing in this function makes that clear to me (unless I'm using [**Solidity Visual Developer**](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=tintinweb.solidity-visual-auditor)). Were this a private audit, I may start an `Informational` section in my `notes.md`. ``` ## About > The project allows users to enter a raffle to win a dog NFT. ## Informational `PuppyRaffle::entranceFee` is immutable and should follow a more clear naming convention ie. `i_entranceFee` or `ENTRANCE_FEE` ``` > **Pro-tip:** In VS Code, you can use these keyboard shortcuts to navigate between previous and next cursor positions: > > - Windows: `Alt + Left/Right Arrow` > - Mac: > - Previous - `Control + '-'` > - Next - `Control + Shift + '-'` ### Wrap Up We're going to be bouncing between `Recon` and `Vulnerability` phases a bit in the Puppy Raffle review. Sometimes the lines can be a little blurry, but you'll find a workflow that works well for you with time and experience. Let's go back to the code.
Follow along with this video:
Starting with the Code
What I like to do when first assessing a codebase is to start at the main entry point. Sometimes this area of a protocol may be a little unclear, but using Solidity: Metrics can help us out a lot.

Pay special attention to the functions marked public or external. Especially those which modify state or are payable. These are going to be certain potential attack vectors.
Note: In Foundry you can use the command
forge inspect PuppyRaffle methodsto receive an output of methods for the contract.
I would start with the enterRaffle function. Let's take a look.
Starting with the NatSpec we may have a few questions rise.
What's meant by # of players?
How does the function prevent duplicate entrants?
Write questions like these in your notes.md or even as @audit notes inline. These are things we'll want to answer as we progress through the code.
One thing I notice in our next few lines is - I don't really love their naming conventions. entranceFee is immutable and nothing in this function makes that clear to me (unless I'm using Solidity Visual Developer).
Were this a private audit, I may start an Informational section in my notes.md.
Pro-tip: In VS Code, you can use these keyboard shortcuts to navigate between previous and next cursor positions:
Windows:
Alt + Left/Right ArrowMac:
Previous -
Control + '-'Next -
Control + Shift + '-'
Wrap Up
We're going to be bouncing between Recon and Vulnerability phases a bit in the Puppy Raffle review. Sometimes the lines can be a little blurry, but you'll find a workflow that works well for you with time and experience.
Let's go back to the code.
Recon: Reading the Code
Navigate PuppyRaffle codebase, player entry points, keyboard shortcuts.
Previous lesson
Previous
Next lesson
Next
Duration: 25min
Duration: 1h 19min
Duration: 35min
Duration: 2h 28min
Duration: 5h 04min
Duration: 5h 23min
Duration: 4h 33min
Duration: 2h 01min
Duration: 1h 41min