5/5
_Follow along with this video:_ --- ### Init State and Axions Welcome back! We're almost ready to start verifying this protocol, but we've left out an important component. As things stand in `GasBad.spec` currently, nothing will work. Unlike Solidity, the ghost variables we've declared aren't initialized with any value. The `Certora Verification Language (CVL)` requires [**Initial State Axioms**](https://docs.certora.com/en/latest/docs/cvl/ghosts.html#initial-state-axioms) in order to assign starting points to our `listingUpdatesCount` and `log4Count` variables. 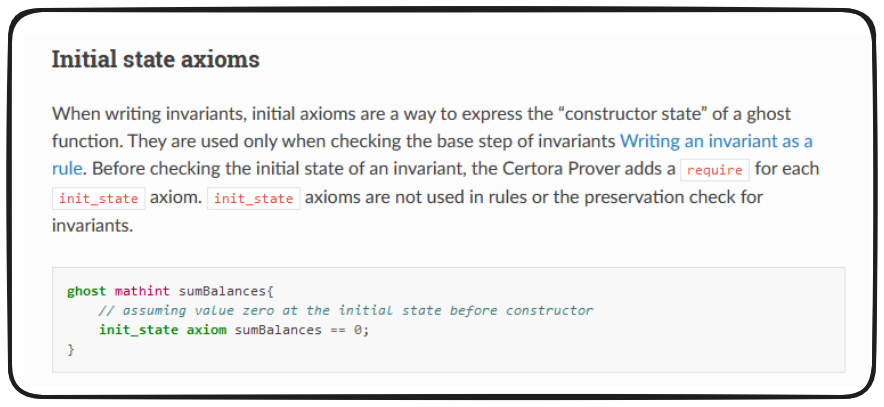 --- #### init_state - Sets the initial state or value of a variable, the starting point #### axiom - declare that something must always hold true. Tells the prover to assume this to always be the case. Acts similar to `require` Let's apply this to our GasBad.spec ghost variables. ```js /* * Verification of GasBadNftMarketplace */ ghost mathint listingUpdatesCount { // initial state will be 0 // require such to be true init_state axiom listingUpdatesCount == 0; } ghost mathint log4Count { // initial state will be 0 // require such to be true init_stat axiom log4Count == 0; } ``` > ❗ **PROTIP** > Try running the prover _without_ initializing these variables. What happens? ### The Rule We now have 2 hooks configured. One is tracking whenever our s_listings storage variable is updated and the other is tracking when our LOG4 events are emitted. All that's missing now is to write the rule/invariant to assert that these match. Because we've set things up with these hooks, we can just write a very simple invariant pertaining to them. ```js invariant anytime_mapping_updated_emit_event() listingUpdatesCount <= log4Count; ``` That's it, that's all we need. The reason we chose `<=` is because there may be other LOG4 emissions we aren't accounting for, when other storage variables are emitted, but this should allow us to verify this one case! > ❗ **NOTE** > In an audit scenario you would **definitely** want to expand on what we've done here, assuring that _any time_ storage is updated an event is emitted, but for simplicity's sake we've pared down our example. ### Wrap Up <details> <summary>GasBad.spec</summary> ```js /* * Verification of GasBadNftMarketplace */ ghost mathint listingUpdatesCount { init_state axiom listingUpdatesCount == 0; } ghost mathint log4Count { init_state axiom log4Count == 0; } hook Sstore s_listings[KEY address nftAddress][KEY uint256 tokenId].price uint256 price STORAGE { listingUpdatesCount = listingUpdatesCount + 1; } hook LOG4(uint offset, uint length, bytes32 t1, bytes32 t2, bytes32 t3, bytes32 t4) uint v { log4Count = log4Count + 1; } /*////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// RULES //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////*/ // It shouldn't be possible to have more storage updates than events invariant anytime_mapping_updated_emit_event() listingUpdatesCount <= log4Count; ``` </details> ### Wrap Up We've taken a bit of an easier approach to things, but that's ok. This is a great stepping stone towards what's more complex. What we've set up here _should_ hold. The number of times storage is updated should always be less than or equal to our `LOG4` count. In the next lesson, let's run the prover and see what happens.
Follow along with this video:
Init State and Axions
Welcome back! We're almost ready to start verifying this protocol, but we've left out an important component. As things stand in GasBad.spec currently, nothing will work. Unlike Solidity, the ghost variables we've declared aren't initialized with any value. The Certora Verification Language (CVL) requires Initial State Axioms in order to assign starting points to our listingUpdatesCount and log4Count variables.

init_state
Sets the initial state or value of a variable, the starting point
axiom
declare that something must always hold true. Tells the prover to assume this to always be the case. Acts similar to
require
Let's apply this to our GasBad.spec ghost variables.
❗ PROTIP
Try running the prover without initializing these variables. What happens?
The Rule
We now have 2 hooks configured. One is tracking whenever our s_listings storage variable is updated and the other is tracking when our LOG4 events are emitted. All that's missing now is to write the rule/invariant to assert that these match.
Because we've set things up with these hooks, we can just write a very simple invariant pertaining to them.
That's it, that's all we need. The reason we chose <= is because there may be other LOG4 emissions we aren't accounting for, when other storage variables are emitted, but this should allow us to verify this one case!
❗ NOTE
In an audit scenario you would definitely want to expand on what we've done here, assuring that any time storage is updated an event is emitted, but for simplicity's sake we've pared down our example.
Wrap Up
GasBad.spec
Wrap Up
We've taken a bit of an easier approach to things, but that's ok. This is a great stepping stone towards what's more complex. What we've set up here should hold. The number of times storage is updated should always be less than or equal to our LOG4 count.
In the next lesson, let's run the prover and see what happens.
init_state and Axioms
Key focus on initializing ghost variables and creating an initial state axiom, writing rules and invariants for storage updates and event omissions to ensure their validity.
Previous lesson
Previous
Next lesson
Next
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Assembly
Writing smart contracts using Huff and Yul
Ethereum Virtual Machine OPCodes
Formal verification testing
Smart contract invariant testing
Halmos, Certora, Kontrol
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Smart contract security researchers
- Advanced Smart contract engineers
- Chief Security Officiers
- Security professionals
Potential Careers
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Meet your instructors
Guest lecturers:
Last updated on August 11, 2025
Duration: 30min
Duration: 4h 39min
Duration: 3h 58min
Duration: 1h 56min
Course Overview
About the course
What you'll learn
Assembly
Writing smart contracts using Huff and Yul
Ethereum Virtual Machine OPCodes
Formal verification testing
Smart contract invariant testing
Halmos, Certora, Kontrol
Course Description
Who is this course for?
- Smart contract security researchers
- Advanced Smart contract engineers
- Chief Security Officiers
- Security professionals
Potential Careers
Security researcher
$49,999 - $120,000 (avg. salary)
Smart Contract Auditor
$100,000 - $200,000 (avg. salary)
Meet your instructors
Guest lecturers:
Last updated on August 11, 2025
