--- ### How AMMs Work Recap Now that we've taken a deep look at an AMM, let's put it all together and recap how they work and the motivations behind them. We started by gaining an understanding of order books and how they work. 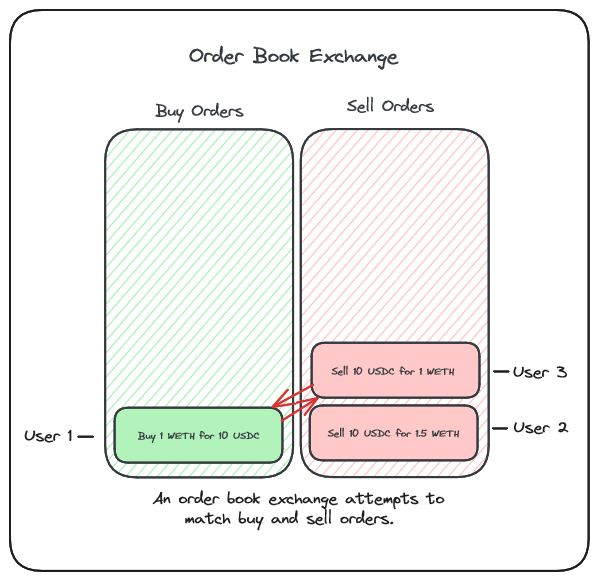 A few characteristics of order book exchanges we covered were: - An exchange tracks desired buy and sell order submitted by users - Matches are attempted to be made between these orders to execute a trade - Each order/trade constitutes a transaction in many cases and gas costs and fees of a system like this can quickly climb - Placing orders and waiting for matches and multiple transactions can be a slow and cumbersome process in DeFi To solve the above problems DeFi introduced Automated Market Makers (AMMs), and they function a little differently. We learnt that AMMs support user trading through the use of Liquidity Pools. As users execute trades via the liquidity pools, the ratio of the assets within the pool is what determines the price of the traded assets, a system of pure supply and demand. 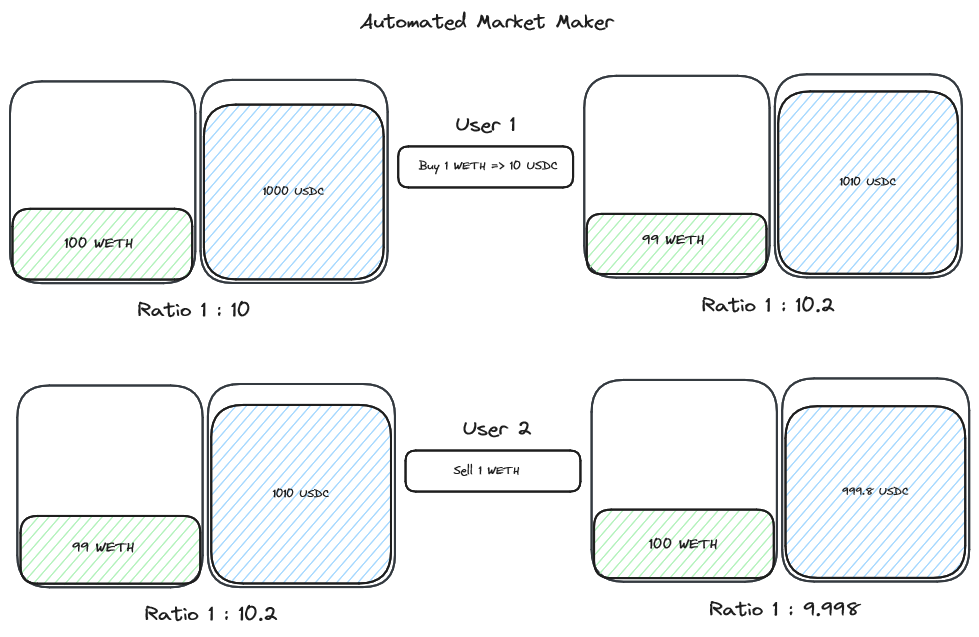 Additionally we learnt the source of these liquidity pools are known as liquidity providers. Liquidity providers are incentivized to add liquidity to a pool though an LP Token system. When liquidity providers deposit funds into a liquidity pool, they often receive LP Tokens, the number of which represents their ratio of contribution to the total pool. 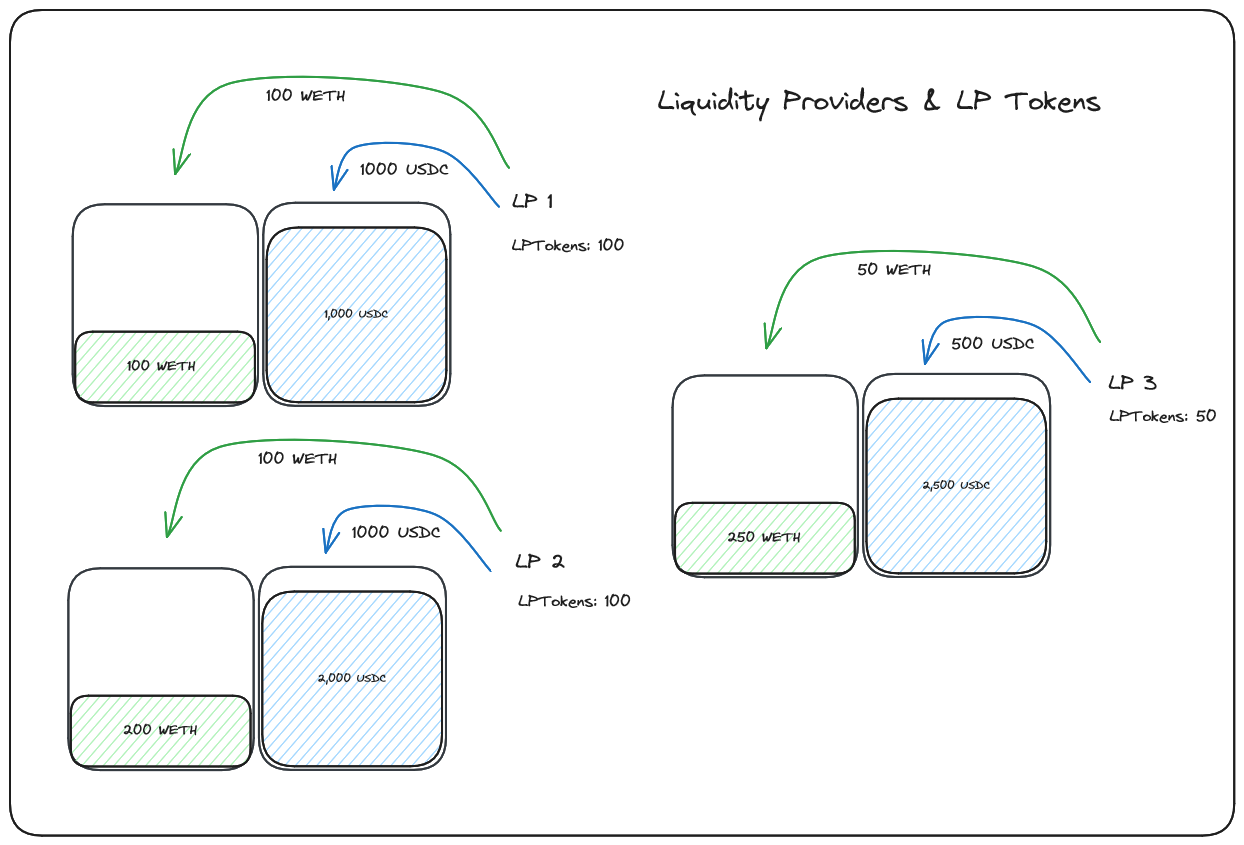 This is where fees come in. Fees are charged for each transaction with the protocol and then added to the appropriate pool. What this means practically for a liquidity provider is that their LP Tokens, representing their percentage claim of the pool, increase in value allowing liquidity providers to profit off of every transaction with the pool! 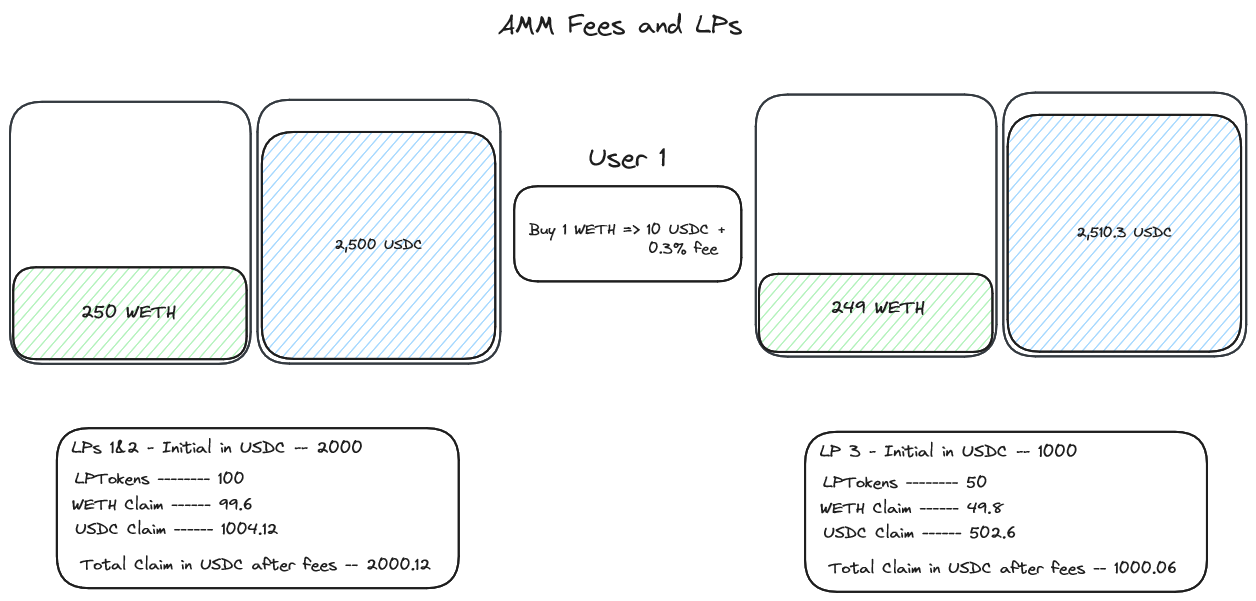 ### Wrap Up Whew! That about sums up AMMs and DEXs from a high level perspective! Remember, this is all about gaining context in our security review. This is a great example of some of the steps a security researcher may need to take to truly understand the scope and purpose of a protocol they're reviewing! Don't hesitate to take a break before we continue on with our TSwap recon in the next lesson.
How AMMs Work Recap
Now that we've taken a deep look at an AMM, let's put it all together and recap how they work and the motivations behind them.
We started by gaining an understanding of order books and how they work.

A few characteristics of order book exchanges we covered were:
An exchange tracks desired buy and sell order submitted by users
Matches are attempted to be made between these orders to execute a trade
Each order/trade constitutes a transaction in many cases and gas costs and fees of a system like this can quickly climb
Placing orders and waiting for matches and multiple transactions can be a slow and cumbersome process in DeFi
To solve the above problems DeFi introduced Automated Market Makers (AMMs), and they function a little differently. We learnt that AMMs support user trading through the use of Liquidity Pools. As users execute trades via the liquidity pools, the ratio of the assets within the pool is what determines the price of the traded assets, a system of pure supply and demand.

Additionally we learnt the source of these liquidity pools are known as liquidity providers. Liquidity providers are incentivized to add liquidity to a pool though an LP Token system. When liquidity providers deposit funds into a liquidity pool, they often receive LP Tokens, the number of which represents their ratio of contribution to the total pool.

This is where fees come in.
Fees are charged for each transaction with the protocol and then added to the appropriate pool. What this means practically for a liquidity provider is that their LP Tokens, representing their percentage claim of the pool, increase in value allowing liquidity providers to profit off of every transaction with the pool!

Wrap Up
Whew! That about sums up AMMs and DEXs from a high level perspective! Remember, this is all about gaining context in our security review. This is a great example of some of the steps a security researcher may need to take to truly understand the scope and purpose of a protocol they're reviewing!
Don't hesitate to take a break before we continue on with our TSwap recon in the next lesson.
How AMMs Work
Patrick further details AMMs and how they function in this quick review on How AMMs Work.
Previous lesson
Previous
Next lesson
Next
Duration: 25min
Duration: 1h 30min
Duration: 35min
Duration: 2h 28min
Duration: 5h 04min
Duration: 5h 23min
Duration: 4h 33min
Duration: 2h 01min
Duration: 1h 41min